, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Vascular Tumors
CD31, CD34, factor VIII, CD105, ERG, podoplanin, thrombomodulin (CD141), and Fli-1 [1].
CD31 (PECAM-1) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: membranous/cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Vascular tumors | Plasmacytoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Langerhans sarcoma, granulocytic sarcoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, rare carcinoma types | Endothelial cells, megakaryocytes/platelets, macrophages/monocytes, Kupffer cells, osteoclasts, myoblasts, granulocytes, mantle zone B cells, T/NK cells and plasma cells |
Positive control: appendix | ||
Diagnostic Approach
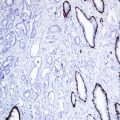
CD31, also known as PECAM-1 (platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1), is a transmembrane glycoprotein and member of the immunoglobulin family normally expressed on endothelial cell junctions and on the surface of platelets, monocytes, granulocytes, and B-lymphocytes. CD31 is a sensitive and specific marker for blood vessels and vascular tumors [1, 2].
Diagnostic Pitfalls
Low expression levels of CD31 are reported in rare nonvascular tumors such as chronic lymphocytic lymphoma, plasmacytoma, Langerhans cell neoplasia, leiomyosarcoma, mesothelioma, and glioma in addition to few carcinoma types such as carcinoma in situ and invasive breast carcinoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma.
CD34 | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: membranous | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Vascular tumors, Kaposi’s sarcoma, GIST, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, solitary fibrous tumor, epithelioid sarcoma, AML (M0), granulocytic sarcoma, neurofibroma, liposarcoma | Pre-B-ALL, AML (M7), alveolar soft part sarcoma, congenital and infantile fibrosarcoma, inflammatory fibrous polyp of gastrointestinal tract, breast fibroadenoma, giant cell fibroblastoma, juxtaglomerular cell tumor, superficial acral fibromyxoma | Hematopoietic progenitor cells (myeloid, B- and T-lymphocyte precursors), endothelial cells, hepatic sinusoidal cells, interstitial cells of Cajal, endometrial stroma, fibroblasts |
Positive control: appendix | ||
Diagnostic Approach
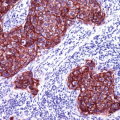
CD34 is a cell surface adhesion glycoprotein expressed on the surface of precursor hematopoietic cells of myeloid and lymphoid lineage, a subset of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial cells, and a large number of tumors originated from these cells. CD34 is a widely used marker to highlight blood vessels and vascular tumors, but it is less specific than CD31 (Fig. 24.1) [1, 2]. CD34 is also an important marker for other tumors such as dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and GIST. Furthermore, CD34 is one of the essential markers for hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells that also label myeloid blast in AML.
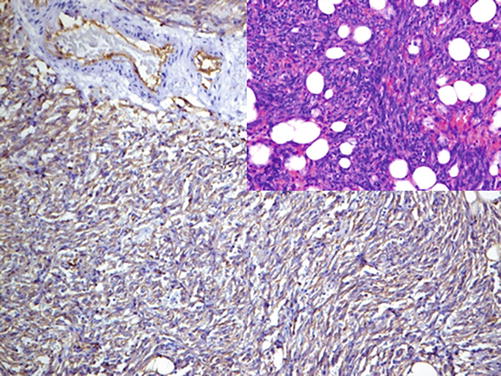

Fig. 24.1
CD34 labeling neoplastic endothelium in angiosarcoma
Diagnostic Pitfalls
Because of its broad expression spectrum, CD34 must be used as a screening marker supported by a panel of more specific antibodies [3].
Factor VIII (von Willebrand factor) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Vascular tumors | Endothelial cells and endocardium, platelets and megakaryocytes, mast cells | |
Positive control: appendix | ||
Diagnostic Approach
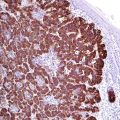
Factor VIII (von Willebrand factor) is a glycoprotein complex composed of three subunits with functional binding domains to platelet glycoproteins, collagen, and heparin. Factor VIII is synthesized by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes and stored in the Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells. Factor VIII is a specific marker for blood vessels and vascular tumors. The intensity of factor VIII expression correlates with the differentiation grade of the vascular tumors and is very low in poorly differentiated vascular tumors such as angiosarcoma (Fig. 24.2).
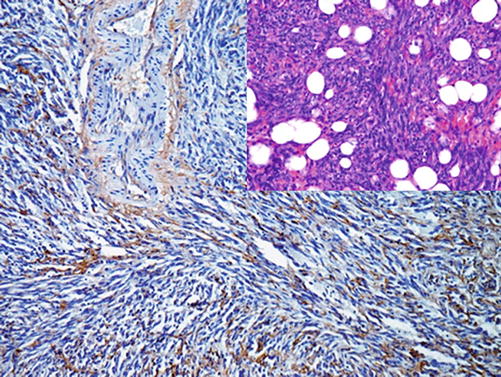

Fig. 24.2
Angiosarcoma with diffuse expression of factor VIII
Podoplanin (D2-40) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: membranous/cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

| |