, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Ewing’s Sarcoma/Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors
CD99, Fli-1, NKX2.2, DAX-1, CD56, chromogranin, and synaptophysin.
CD99 (MIC2) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: membranous/cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET, T- and B-ALL, solitary fibrous tumor | T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, AML, GIST, various carcinomas including the breast and prostate and hepatocellular carcinoma, thymoma, ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors, synovial sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, atypical fibroxanthoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, endocrine and neuroendocrine tumors, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, Wilms’ tumor, melanoma, nephroblastoma, ependymoma, mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, extrarenal malignant rhabdoid tumor, meningeal hemangiopericytoma | Cortical thymic lymphocytes, T cells and activated B cells, ovarian granulosa cells, Sertoli cells, pancreatic islet cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, ependymal cells, urothelium |
Positive control: PNET | ||
Diagnostic Approach
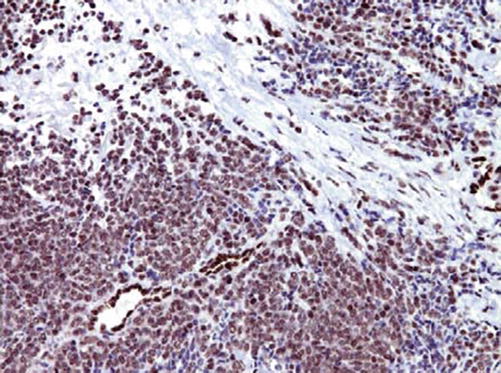
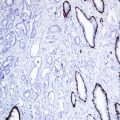
CD99 (known as MIC2 or E2 antigen) is a cell surface glycoprotein expressed on the surface of cortical thymocytes and subset of mature T- and B-lymphocytes. CD99 plays a role in T-cell adhesion and leukocyte migration and extravasation. CD99 has a broad expression spectrum and found in a large number of normal and neoplastic cells. CD99 is widely used as a marker for Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET family exhibiting a membranous stain, while a cytoplasmic stain can be noted in other tumor types. CD99 is negative in neuroblastoma (Fig. 28.1).

Fig. 28.1
Ewing’s sarcoma with strong membranous CD99 expression
Diagnostic Pitfalls
As listed in the table above, CD99 has a very wide expression spectrum and low specificity; consequently CD99 should never be used as a single marker for tumor diagnosis, especially in tumors with similar morphology such as PNET and ALL [1, 2]. A panel of more specific antibodies must be always used to confirm the diagnosis.
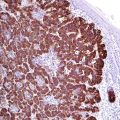
Fli-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: nuclear | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Ewing’s sarcoma, vascular tumors | Lymphoblastic lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic lymphoma, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, Merkel cell carcinoma, melanoma | Endothelial cells, T-lymphocytes |
Positive control: endothelial cells | ||
Diagnostic Approach
Fli-1 gene (friend leukemia virus integration site 1, also known as transcription factor ERGB) is a member of the ETS proto-oncogene family functioning as a transcriptional activator highly expressed during embryogenesis. The Fli-1 gene is the translocation partner in the t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation, the most common and the most specific molecular marker for Ewing’s sarcoma/PNET family that is found in more than 90% of the cases. Available antibodies to Fli-1 gene product found to be of high specificity for the PNET family (Fig. 28.2