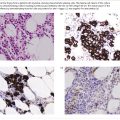
Lymphoma is a clonal neoplastic proliferation of lymphoid cells. There are many different types divided into two main groups (Box 31.1): Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The NHLs are further subdivided into B-cell diseases (85% of cases) and T-cell diseases (15%) and each of these groups contains many different types.
Box 31.1 The World Health Organization (WHO) 2008 classification (simplified).
Mature B-cell neoplasms
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
B-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Hairy cell leukaemia
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinaemia
Plasma cell myeloma
Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT-lymphoma)
Nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma/leukaemia
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. These are usually B-cell and may be polyclonal or clonal (lymphomas)
T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree