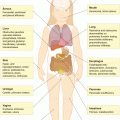
Chemotherapy
Dose
Late effect
Baseline screening
Anthracycline
≥300 mg/m2 or
Cardiomyopathy valvular, pericardial damage, coronary artery disease
EKG, ECHO
(Doxorubicin
>200 mg/m2 +
Daunorubicin
Chest XRT ≥30 Gy
Epirubicin
HD CTX (120–200 mg/kg)
Mitoxantrone
Idarubicin)
Acute myeloid leukemia
CBC
Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
>7.5 gm/m2
Gonadal failure
FSH, LH, estradiol/testosterone
Cardiomyopathy
EKG, ECHO
Second cancersa
CBC, UA
Nephropathy/bladder irritation
Serum electrolytes, UA
Ifosfamide
≥60 gm/m2
Nephropathy
Serum electrolytes, UA
Second cancersa
CBC, UA
Gonadal failure
FSH, LH, estradiol/testosterone
Etoposide
>3.5 gm/m2
Leukemia
CBC
HD MTX b with IT chemo
>1 gm/m2
Neurocognitive
Neurocognitive testing
Deficits,
Leukoencephalopathy
Hepatic fibrosis (MTX)
LFTs, bilirubin
Bleomycin
>400 U
Pulmonary toxicity
PFT, CXR
Cisplatin
≥360 mg/m2 or
Ototoxicity
Audiogram
<360 mg/m2 +CXRT
Glomerular, tubular Dysfunction, Low Mg
UA, electrolytes
Dyslipidemia
Fasting Lipid panel
Table 4.2
Cumulative dose ranges of common chemotherapy agents based on current COG protocols for each diagnosis
Chemotherapy | ALL | AML | STS | EWS | Osteosarcoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Anthracycline | 75–300 mg/m2 | 450 mg/m2 | 375–450 mg/m2 | 375 mg/m2 | 375–450 mg/m2 |
Doxorubicin | |||||
Daunorubicin | |||||
Idarubicin | |||||
Mitoxantrone | |||||
Cyclophosphamide | 1–4 gm/m2 | 4.8–16.8 gm/m2 | 8.4 gm/m2 | ||
Ifosfamide | 9 gm/m2 a | 63 gm/m2 | 48–51 gm/m2 | ||
Etoposide | 1 gm/m2 a | 1.5 gm/m2 | 0–2.5 gm/m2 | 3.5 gm/m2 | 1.5 gm/m2 |
Table 4.3
Isotoxic dose conversion of anthracyclines based on current Children’s Oncology Guidelines
Anthracycline | Conversion |
|---|---|
Doxorubicin | Multiply by 1 |
Daunorubicin | Multiply by 0.833 |
Epirubicin | Multiply by 0.67 |
Mitoxantrone | Multiply by 4 |
Idarubicin | Multiply by 5 |
Table 4.4
Leukemia follow-up
Evaluation | Baseline off therapy | LTFU 2 years | 3 years | 4 years | 5 years | 6 years | 7 years | 8 years | 9 years | 10 years | 11 years | 12 years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Date | ||||||||||||
History, physical and exam | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
CBC, BUN, Crt, LFTs, UA, TSH, FT4, ferritin (baseline only) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Fasting glucose and lipid profile every 3–5 years and at entry to LTFU | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
Girls: FSH, LH, estradiol | ||||||||||||
Boys: LH, FSH, testosterone | ||||||||||||
Baseline at age >13 and for delayed puberty, s/sx of estrogen/testosterone deficiency | ||||||||||||
EKG, ECHO | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
Total anthracycline ≥300 mg/m 2 (yearly) or <300 mg/m 2 (every 3–5 years and at entry to LTFU) | ||||||||||||
DEXA scan | ||||||||||||
Baseline at age 18 years, consider earlier if clinically indicated | ||||||||||||
Neuropsychological evaluation | X | |||||||||||
Baseline and then PRN | ||||||||||||
Ophthalmology | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Dentist every 6 months | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
If patient has sx of Osteonecrosis, | ||||||||||||
MRI/orthopedic referral | ||||||||||||
Monitor for obesity, second cancers | ||||||||||||
Craniospinal XRT: monitor growth curve, IGF-1, IGFBP3, scoliosis |
Table 4.5
Hodgkin lymphoma follow-up
Evaluation | Baseline off therapy | LTFU 2 years | 3 years | 4 years | 5 years | 6 years | 7 years | 8 years | 9 years | 10 years | 11 years | 12 years | 13 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Date | |||||||||||||
History, physical and exam | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Chest XRT—include clinical breast exam | |||||||||||||
CBC, BUN, Crt, LFTs, TSH, FT4, ferritin (baseline only) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Fasting glucose and lipid profile every 3–5 years and at entry to LTFU | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
Girls: FSH, LH, estradiol | |||||||||||||
Boys: LH, FSH, testosterone, semen analysis PRN | |||||||||||||
Baseline at age >13 and for delayed puberty, s/sx of estrogen/testosterone deficiency | |||||||||||||
CXR (every 3–5 years to rule out fibrosis) | X | ||||||||||||
EKG, ECHO | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
Total anthracycline ≥300 mg/m 2 (yearly) or <300 mg/m 2 (every 3–5 years and at entry to LTFU) | |||||||||||||
Pulmonary function test (every 3–5 years or more frequently if clinically indicated) | X | X | X | ||||||||||
DEXA scan | |||||||||||||
Baseline at age 18 years, consider earlier if clinically indicated | |||||||||||||
Neuropsychological evaluation | X | ||||||||||||
Baseline and then PRN | |||||||||||||
Ophthalmology | X | X | X
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|