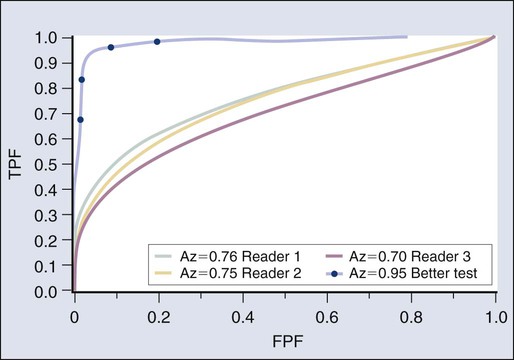
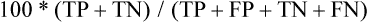• Noninvasive medical imaging often is essential to cancer management at multiple times in the course of the illness. • Imaging currently is used for screening to detect cancer, characterize lesions, perform locoregional and systemic staging, provide prognostic information, assess response during and after therapy, restage after treatment, perform follow-up of patients for recurrence, and precisely guide biopsies and therapies such as external beam or systemic radiation, brachytherapy, or thermal and other ablations. • More invasive interventional radiologic procedures also can guide and monitor vascular or intraluminal delivery of treatments such as radioactive microspheres, embolic materials, radiofrequency or cryoablation, and therapeutic drugs. • Imaging methods range from the traditional anatomic methods—radiograph, computed tomography (CT), and ultrasound—to the more functional methods of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear medicine methods, including positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and planar nuclear imaging. Hybrid methods combining PET and CT, SPECT and CT, and PET and MRI are growing in importance. Optical imaging is promising but is limited by penetration of light through tissues to superficial structures in most cases. • Plain films and mammography remain useful techniques, with mammography (including digital mammography) being the main imaging method that has been clearly proven capable of reducing cancer deaths when applied in the screening setting. • CT remains the cornerstone technology for most oncologic imaging, and CT technology that allows for rapid-sequence angiography is finding new applications, as is three-dimensional reconstruction of CT data sets. Screening data with CT-colonography continues to improve, and in some studies it has been found to be comparable with traditional colonoscopy for colon cancer screening. CT scanning for lung cancer screening appears to be capable of reducing lung cancer death rates when applied to high-risk populations. The radiation dose from CT is a concern, and major efforts to reduce this dose from CT scanning have been implemented in newer CT systems. • MRI is the imaging tool of choice for central nervous system, spinal, and musculoskeletal neoplasms, as well as for assessing vascular and some hepatobiliary and pelvic lesions. MRI also can be used to detect breast cancers, especially in women with dense breasts. Concerns regarding gadolinium-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis have led to cautions in the use of MRI contrast medium in patients with impaired renal function. Newer MRI techniques such as diffusion imaging and complement diffusion contrast MRI appear promising in assessing response to tumor treatment. • Bone scans using single-photon methods (e.g., technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate) remain the dominant procedure for detecting suspected bone metastases; however, the PET agent fluorine-18 sodium fluoride is increasingly being applied. These techniques may be less sensitive for marrow involvement than MRI and other PET techniques for detecting bone metastases of many tumors. • PET and PET/CT technology using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) continues to grow in a wide variety of applications, and its use is becoming increasingly routine in the management of patients with cancer at varying states of the disease process. PET is used with increasing frequency in the staging and follow-up of lung, colorectal, and head and neck cancers, as well as lymphomas and other types of tumors, and it is now a routine tool in lymphoma management at several points in the disease. PET with non-FDG tracers is a promising research area with growing clinical applications. In particular, progress has occurred in imaging of prostate cancer with several imaging agents, including U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved carbon-11 choline. • The fusion of anatomic and functional images to create hybrid “anatomolecular images” with software or dedicated instruments such as PET/CT, SPECT/CT, or the newer PET/MRI devices also is seeing rapid growth in applications in cancer imaging. Fully diagnostic CT scans coupled with PET imaging in the form of PET/CT often provide valuable composite imaging for cancer management. PET/MRI is an evolving technology, and several technical approaches are in clinical use at select medical centers. • Imaging management for staging lung cancer and characterizing solitary pulmonary nodules often includes FDG-PET in addition to CT when the technology is available because PET-CT has high accuracy in lung cancer assessments compared with CT. • Imaging management of suspected recurrences of colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer, lymphoma, and many other cancers often now includes the use of PET in addition to CT. Response criteria for FDG-avid lymphomas are now mainly PET-based, and PET assessments of treatment response are increasingly applied. Use of PET at earlier stages in the workup is becoming increasingly common, as is the use of PET in early assessments of the efficacy of cancer therapies. Adapting treatments based on the response seen on PET/CT is also increasingly applied. • In prostate cancer, available imaging methods remain suboptimal for the detection of primary tumor and early determination of local or systemic tumor spread. MRI nodal contrast agents are promising but not yet routinely available, and MR spectroscopy has had only limited success in the prostate. A variety of MRI sequences, including T2 images, diffusion images, and diffusion contrast enhanced MRI may improve upon purely anatomic MRI approaches for lesion detection and detection of extracapsular involvement. A variety of innovative radiotracers for PET show promise for detecting disease recurrence, and 11C choline is now approved by the FDA in the United States for use in persons with prostate cancer. • Visceral angiography for diagnostic purposes is being supplanted by CT and MRI methods; however, it remains important as a tool for intravascular delivery of therapies such as chemotherapy, coils, or radioactive microspheres. • CT, ultrasound, fluoroscopy, and innovative MRI systems can guide interventional procedures such as thermal and cryotherapeutic lesion ablations. • Highly specific probe-reporter systems are being developed to allow for optical and radionuclide imaging of transfected gene biodistribution and function. These approaches face major regulatory challenges when being translated to humans. • Combined anatomic and functional information is being applied to allow for more precise planning of external beam radiation therapy, including intensity-modulated radiation therapy and conformal therapy, which are methods that potentially allow for increasing dose escalation and minimization of toxicity to normal tissues. • Emerging imaging methods are proving increasingly useful in providing information on the physiology and molecular characteristics of lesions, which means that a multiparametric biological imaging phenotype for tumors can be obtained, making it possible to display heterogeneities in tumors. This phenotype can more precisely guide individualized tumor treatment to yield a higher probability of success without excessive toxicity for treatment of the selected neoplastic process. Specific clinical questions addressed by imaging include screening for the presence of cancer, characterizing anatomic lesions as malignant or benign, and staging a neoplasm—that is, determining the size and local extent of a primary lesion and determining whether it is localized or locoregionally or systemically metastatic. Such studies are essential for determining whether the patient is a candidate for surgical resection, identifying the extent of the field for radiation therapy, and determining whether systemic chemotherapy is appropriate. Initial staging of tumor size and extent also can provide important prognostic data. During the course of treatment, imaging is used to determine the response of the cancer. Imaging also is often used to monitor patients for recurrence or the development of second malignancies. Imaging is being used more often as a method to assist in the delivery of minimally invasive therapeutic procedures to ablate cancers, guide radiation therapy, and guide the dosing of therapeutic drugs, including radiopharmaceutical agents, more precisely.1 It can sometimes be difficult to judge how “good” a test is by reading the literature. Sensitivity is supposed to be substantially independent of study composition, but as discussed in the next section, certain imaging tests may be insensitive for some very early-stage disease but very, very sensitive for more advanced disease. Each imaging test has a limit of detection threshold below which tumors cannot be detected because they are not distinguishable from the background tissues. Thus the patient population and, very often, the tumor burden and average tumor size can make a difference in the sensitivity of a test for the detection of cancer. Virtually all noninvasive imaging tests are less sensitive for small-volume disease than for large-volume disease. For example, if an imaging test is used in a patient population in which patients have advanced disease before seeking medical attention (e.g., they are symptomatic at presentation), the imaging test may have far greater sensitivity than if it were used in patients with earlier stage, smaller tumors. For example, positron emission tomography (PET) with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) has been reported to be more than 90% sensitive for detecting metastatic melanoma, but it is less than 20% sensitive in detecting early (low tumor volume) nodal metastases of melanoma at initial surgical resection. Mammography has higher sensitivity in women with more radiolucent than radiodense breasts. A test with high sensitivity has a low number of false-negative results.2 The false-negative fraction usually is expressed as 1− sensitivity (in this case, sensitivity being rated on a 0-1 scale).3 Again, specificity can be calculated on a per-patient basis, a per-lesion basis, or a per-region basis. The per-patient calculations commonly are performed in the screening setting. They also can be done per region of the body (e.g., Is the liver free of tumor? Are the draining lymph nodes free of tumor?). It is technically difficult and sometimes impossible to know exactly how many tumor foci are present, because this depends on the reference gold standard. It is not possible to do “whole body” biopsies antemortem, and thus some very small tumor foci may not be known to be present when disease is diagnosed. Specificity can be affected substantially if the imaging test is used in a population that has a characteristic that can result in false-positive results for the imaging test. For example, inflammatory and infectious lung disease, such as active tuberculosis or sarcoidosis, if present in a patient population, can result in false-positive findings on PET or computed tomography (CT) scans or other imaging methods. In this situation, the specificity of FDG-PET, and likely of CT, for staging the mediastinum for cancer would vary. Thus the specificity of PET for assessing mediastinal lymph nodes may be much lower in areas of the world with endogenous tuberculosis than in developed areas without it. Therefore an imaging test that is very useful in one part of the world may be far less useful in another part of the world. A highly specific test has a low frequency of false-positive results (i.e., a low frequency of positive test results in the patient population that does not have the disease). The ideal imaging test has both high sensitivity and high specificity, although none of our current imaging tests has perfect sensitivity and specificity.2 Thus a test that is effective in a patient population with a high prevalence of a disease may be far less valuable in a patient population with a lower prevalence of the same disease, because there would be far too many false-positive results. The most effective use of imaging technology is in groups of patients in whom the imaging characteristics are expected to be robust enough to allow for predictions in individual patients. These challenges are particularly apparent when a test that was developed and validated in a patient population with disease is used to evaluate individuals with a lower prevalence of tumor (i.e., screening). In this situation, the number of false-positive findings may rise dramatically, sometimes nearly completely negating the value of the test.4 Cancer imaging tests are interpreted by imaging specialists, who are often radiologists. As with all of medicine, considerable science is involved in image interpretation, but the human element, or “art” as it is referred to in some settings, also is involved. In developed countries, medical specialty boards have been established to ensure that practitioners have a base level of training and knowledge, thereby providing some level of uniformity to the interpretation of images. However, even with board certification and extensive training, not all imaging specialists interpret a given imaging study in the same manner. Thus although the goal of an imaging test often is a simple binary “yes, there is tumor” or “no, there is no tumor” answer, varying degrees of certainty exist in the interpretation of an image in most instances. Some readers read with high sensitivity, whereas others read with high specificity. Unless a test is very robust, it is difficult to achieve both high sensitivity and high specificity.5 An example of a receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve is shown in Figure 18-1. This set of curves reflects the performance of PET imaging in detecting axillary metastases in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. The axes of the curves are the true-positive fraction (sensitivity/100), which forms the y axis, and the false-positive fraction (1—specificity/100), which forms the x axis, on a scale of 0 to 1. A perfect diagnostic test would yield no false-positive or false-negative results. The greater the area under an ROC curve, the greater the accuracy of the test. The results shown in Figure 18-1 are from three readers who graded PET scans using a five-point certainty scale (i.e., not a simple yes/no but a continuum from definitely abnormal to definitely normal). The three readers had similar ROC curves, indicating that they were of generally comparable accuracy. For the same test, however, two readers may be reading at different points on the ROC curve, meaning that one is more sensitive and one is more specific, but both are of equal accuracy. An excellent reader may have a greater area under the ROC curve than a less skilled reader, meaning that the more experienced (and hopefully more capable) reader is both more sensitive and more specific than a less experienced (and presumably less capable) reader. However, virtually none of our imaging tests is perfect, and varying “cut points” between disease and normalcy often are made, affecting the overall performance of the test. In this study, the area under the curve (AUC) of 0.7 to 0.76 was not viewed as sufficiently good for the task of nodal detection of metastatic cancer spread to the axilla.5 Despite this, a very high sensitivity or a very high specificity can be achieved depending on which part of the curve one operates in. A higher, hypothetical curve, with an AUC of 0.9, is shown for a more robust test, such as a higher resolution PET system devoted to imaging the axilla. In practice, sentinel node sampling, which often is guided by imaging or a radionuclide-sensitive probe system, is assuming a very important role in this area of tumor staging.6 Practically, if a rather insensitive test has a high positive predictive value, then the test may be of value if positive but of little value if negative. For example, a strongly positive PET scan for axillary metastases may obviate the need for a pretreatment axillary dissection in a patient with newly diagnosed advanced breast cancer in whom neoadjuvant chemotherapy could be given. Although sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy commonly are used to characterize the tumor detection process, other metrics may be of greater importance. For example, some studies have focused on how often imaging substantially changes management. This type of study is of great practical interest, but the optimal methods to assess such changes in treatment decisions are evolving. Ideally one would like to show that the use of imaging, especially a new imaging technology, when applied randomly to half of the study population, provided a reduction in the number of adverse events in the imaged population, improved survival, or had comparable outcomes at lower costs than standard treatments. As an example, a reduction in the number of “futile thoracotomies” has been used as a metric of success for PET versus CT in planning the treatment of newly diagnosed lung cancer.7 Ideally, randomization of patients to imaged versus not imaged groups can be shown to improve survival. Performance of randomized trials in which a portion of the patients undergo imaging and the other patients do not undergo imaging (or they obtain different types of imaging), with an end point of survival, will be of great interest. Unfortunately, such studies are complex or impossible, because management of patients after imaging may be altered markedly on the basis of imaging results. Thus it can be difficult to separate the imaging study effect from the treatment effect. Ultimately, however, for some imaging studies to be adopted, such evaluations of survival will be needed. This point is particularly relevant to screening, as will be discussed later. Recently, registry data have been applied with substantial benefit to determine if planned or actual patient management is altered through the use of imaging tests. The National Oncologic PET Registry has provided a great deal of information on the use of FDG-PET imaging in the management of patients with a variety of cancers. The National Oncologic PET Registry collected questionnaire data from referring physicians on intended patient management before and after PET. After 1 year, the cohort included data from 22,975 studies (83.7% PET/CT) from 1178 centers. Overall, physicians changed their intended management in 36.5% (95% confidence interval [CI] 35.9-37.2) of cases after PET, supporting the usefulness of PET for cancer imaging in registry cases, which are from a wide range of sources.8 Screening programs for cancer often have taken the form of laboratory tests such as the Papanicolaou (Pap) smear, or, more recently, blood tests for tumor markers. The success of the Pap smear in reducing mortality rates from cervical cancer is incontrovertible. The use of imaging in screening for cancer is an example of success and considerable interest, but also a source of considerable controversy. As discussed in detail in the chapters on breast cancer (see Chapter 91) and lung cancer (see Chapter 72), screening programs have been shown to be capable of saving lives in women older than 50 years. These programs also may save lives in women 40 to 50 years of age, but the data are less compelling.9 Studies have been initiated in which CT scanning is used in an attempt to detect early lung cancer.10 Screening high-risk populations with CT imaging has recently been proven to reduce lung cancer–specific mortality in the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST). This finding follows results from the Early Lung Cancer Action Project (ELCAP), a large study screening patients at increased risk of lung cancer with low-dose CT, which reported promising results in 1999.11 The ELCAP showed that lung cancers are detected at a smaller size and that patients whose cancers are detected by screening live longer after diagnosis than do patients whose tumors are not detected by screening. Whether this outcome translates into longer-term survival for the screened population remains unclear. The ELCAP study further evaluated 31,567 asymptomatic persons at risk for lung cancer using low-dose CT from 1993 through 2005 and from 1994 through 2005; 27,456 repeated screenings were performed.12 A diagnosis of lung cancer was made in 484 participants based on screening. Of particular note, 412 patients (85%) had clinical stage I lung cancer. Ten-year survival approached 90% in this group.11,12 This study demonstrated that annual spiral CT screening can detect lung cancer that is curable. Another large randomized trial of lung cancer screening, the NLST, was reported in 2011.13 In this trial, 53,454 persons at high risk for lung cancer were enrolled from more than 30 U.S. sites. Study participants were randomly assigned to undergo three annual screenings with either low-dose CT (26,722 participants) or single-view posteroanterior chest radiography (26,732). In the CT-screened and chest radiograph–screened groups, 24.2% and 6.9%, respectively, had positive screening studies at some point. A high false-positive screening rate occurred; 96.4% of the positive screening results in the low-dose CT group and 94.5% in the radiography group were false positives. The incidence of lung cancer was significantly higher (1060 vs. 941 cancers) in the low-dose CT group compared with the chest radiograph group. There were 247 deaths from lung cancer per 100,000 person-years in the low-dose CT group and 309 deaths per 100,000 person-years in the radiography group, representing a relative reduction in mortality from lung cancer with low-dose CT screening of 20.0% (95% CI 6.8-26.7; P = .004). The rate of death from any cause was reduced in the low-dose CT group compared with the radiography group by 6.7% (95% CI 1.2-13.6; P = .02). • The cancer must have a considerable public health effect. • The disease must have an asymptomatic period in which detection by imaging is possible. • A therapeutic intervention that should lead to better survival or quality of life must be available. • The prevalence of the disease must be sufficient in the population being screened to justify screening (especially the cost). Low prevalence of disease lowers the positive predictive value of positive scans. • Medical treatment, surgery, or other treatment must be available for the early-stage cancer identified by screening. • The screening test itself must not cause disease at a significant rate. • There must be a high likelihood that the patients in whom early cancer is identified by image-based screening will go on to have a suitable therapeutic intervention. Further, the imaging test itself must be acceptable to patients (in terms of level of discomfort and cost), and it must be sufficiently sensitive to identify cancer often and sufficiently specific to minimize false-positive results. Finally, the costs of the screening process—and attendant costs related to false-positive examinations—must be compatible with the economic resources of the society or individual, and the screening procedure must pose little or no risk to the patient.4 Another important consideration in screening programs is lead time bias. This concept, simply stated, indicates that if the natural history of a disease is unchanged, but the diagnosis is made earlier in the course of the illness, the apparent survival will be improved. For example, let us assume that tumor X has a 6-year natural history from its beginning until the death of the patient, and that treatment is ineffective. The disease might become clinically detectable after 4 years and lead to death in 6 years, with a 2-year survival after diagnosis. With screening, if the tumor is detected 3 years after the onset of disease and no improvement in treatment occurs, then the survival in the screened population would appear to increase from 2 to 3 years after diagnosis. This illusion of improved survival in the screened population is a considerable concern and can lead to inappropriate enthusiasm for screening programs.4 Another important consideration in screening is the possibility of length bias, which is a more complex concept, but it may be related to the types of cancer that can be detected by screening programs. A possibility is that very rapidly growing and presumably highly lethal cancers are less likely to be detected by annual screening programs, whereas more slowly growing cancers, which have an intrinsically better prognosis, may be detected more frequently by screening. In fact, some of the early cancers discovered by screening may not be biologically relevant at all. If so, the patients with cancers identified in the screened population could appear to have a better survival than the patients with cancers identified in the unscreened population, as is the case for prostate cancer screening by prostate-specific antigen (PSA), for example, for which major concerns exist regarding overdiagnosis of slow-growing cancers that are presumed to be indolent and might not require surgery.14 A third factor is the selection bias that is difficult to control for in retrospective observational studies—that is, how the patients and their referring physicians determined that a scan should be performed. Selection bias occurs when unintended differences exist between the groups observed that—while associated with the variable used to sort the groups (for example, exposure in case-control studies and outcome in cohort studies)—affect measurement of the study variable.15 For instance, in a case-control design on the effects on disease-specific mortality of a particular screening program, investigators would examine records from patients who have died from the disease in question versus those who have not died, and then determine the rates of the screening intervention in these two populations. The determination of whether a screening program is valuable to society is often, in part, based on its cost and benefit. The concept of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) often is applied. This concept is defined as the economic cost to society required to result in 1 additional year of quality life for a member of the society. In many Western countries, a figure of $50,000 has been considered a useful guide, with QALYs costing less than this amount considered cost-effective. Such a guideline, however, does not necessarily apply when individuals make their own determinations about whether to pay for a screening test. For example, it is reasonable to expect that persons with greater disposable income would be willing to pay more per QALY than would persons with less disposable income. Thus it can be difficult to generalize about the cost efficacy of screening procedures.16 Noninvasive imaging methods in humans cannot detect and localize a single malignant cell, although flow cytometric methods are very sensitive for finding a very few cancer cells in a patient’s blood, and investigators have a great interest in assays for circulating tumor cells and for tumor DNA and RNA in the blood. Imaging methods are improving, however, and detection of a much smaller number of cells is possible in small animal models. It has been estimated that by the time a tumor reaches 3 to 5 mm in diameter, which is the lower limit in size for detection by the best current noninvasive methods in humans, the tumor has undergone more than 25 doublings and contains 0.1 to 1 billion cells, depending on their size.1 In contrast, a cytologist, on a very good day, or with flow cytometric methods, may be able to identify a single cell as malignant using a microscope. Broadly stated, cancer imaging can be performed using anatomic or functional (“molecular”) imaging methods.1 The traditional imaging of the patient with cancer, and the most established methods, are based on anatomic imaging. However, interest is increasing in more functional methods in cancer imaging. Further, several anatomic imaging methods offer functional components that complement the anatomic method. Hybrid images, derived from and displaying both functional and anatomic data, also are becoming more widely available, often coming from the same hybrid imaging machine, such as PET/CT.17,18 Imaging data are increasingly digital or digitized and suitable for postprocessing and image exchange. The major imaging modalities are discussed in the following section. Plain radiographs offer exceptional resolution but provide relatively little image contrast if not much calcium is present. The radiation dose from a plain film radiograph depends on which portion of the body is being examined. In most centers, plain film radiographs for cancer management are being used less often, with CT scanning increasingly replacing radiographs in the abdomen and MRI in the brain and extremities.19 The recent Digital Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial, which included nearly 50,000 women, showed comparable overall accuracy between film screen and digital mammography in the overall study. A higher accuracy for cancer detection in women younger than 50 years, women with radiodense breasts, and pre- and perimenopausal women was seen with digital mammography compared with film-screen mammography.20 Despite this higher accuracy, the reported sensitivity for both techniques for cancers was only 41% with a positive predictive value of 12%, albeit with 98% specificity, which is far from an ideal performance for a screening test. The move to digital mammography is in part to increase diagnostic accuracy but also to allow digital images to be viewed on picture archiving and communication system, as is the case with virtually all other diagnostic imaging methods in more and more imaging centers.20,21 A newer technique, tomosynthesis, is under evaluation in which a number of “slices” of the breast are generated during a mammographic image acquisition, which involves a moving x-ray source. This approach offers considerable promise going forward but is early in its evolution technically. It has recently received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and will likely improve upon the performance of mammography.22 The cost efficacy of such an approach continues to evolve. Although CT is an exceptional technique, it remains a predominantly anatomic imaging method. Although the timing of intravenous (IV) CT contrast enhancement can provide information, such as the ability to estimate tumor blood flow, it is not easily extracted without a substantial radiation dose from repeated images. Thus only a limited number of post-IV contrast images are obtained with CT to limit radiation dose. All CT images are digital. The large amount of image data generated for analysis with CT also poses a major challenge, because fully interpreting the data can be a lengthy process.23 Angiography has high resolution but typically delivers a high dose of radiation energy to the patient. The use of angiography remains essential for studies to evaluate gastrointestinal bleeding, but with CT angiography continuing to improve in quality, the use of diagnostic angiography has become less frequent in routine clinical practice.24 Ultrasound provides real-time imaging capability to guide biopsies and procedures effectively. Ultrasound is less effective in the evaluation of deeper structures and requires access to a sonographic window; thus it has only a modest role in evaluating deep abdominal structures. Ultrasound is used commonly in evaluations of the pelvis, neck (including the thyroid), and gallbladder and liver areas. Agents that can enhance the visualization of vessels or can be specifically retained in clots are under evaluation, suggesting that ultrasound can offer some functional information beyond that which is purely anatomic.25 Ultrasound contrast agents are being applied to a limited extent. Currently, these agents are mainly for intravascular use. High-energy focused ultrasound remains under development as a tool to ablate, or at least deliver thermal energy to, tumors with therapeutic intent. Ultrasound coupled with needle aspiration biopsy has been used in some settings as a minimally invasive procedure to characterize nodal metastases. Ultrasound combined with mammography also is being evaluated as a screening method for breast cancers, but results in high-risk patients have shown disappointingly low detection rates relative to MRI.26 In many clinical settings, MRI, as applied in imaging for most cancers, is used predominantly as an anatomic imaging method that does not use ionizing radiation. MRI offers superb contrast resolution between tissues and excellent spatial resolution. MRI also offers a variety of forms of functional information. However, it does not offer the level of temporal resolution, in general, that is seen with ultrasound, fluoroscopy, or recent-generation, multiple-slice CT scanners. However, MRI technology has moved forward inexorably, and rapid-pulse sequences allowing gating of images now are available for several types of scanners. MR images can be of a variety of pulse sequences, allowing visualization of several parameters. However, visualization of hydrogen nuclei is the major approach with conventional 1.5 tesla (T) and 3 T machines. Visualization of blood (especially with contrast materials such as gadolinium chelates) and of altered vascular permeability is routinely applied.27 In magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), tissue characterization can be achieved by sampling its magnetic spectrum at 1.5 T. More and more scanners now provide a 3 T or higher field strength signal for evaluation, offering the possibility of more refined tissue characterization. Opportunities to detect increased content of choline (which often is increased in tumor foci) versus other substituents can be helpful in separating tumor from nonmalignant tissues in the brain and elsewhere. Spectroscopy also can provide information on lactate concentration and pH, among other parameters. A limitation of spectroscopy is resolution, which typically is not nearly as fine as that of MRI itself. Thus spectroscopy has only limited application in most oncologic practices.28 Recently, diffusion MRI has shown promise in tumor response assessment, which depends on the freer movement of nuclei in areas of necrosis compared with the motion of nuclei in fully viable tumors. This technique is demonstrating considerable potential for response assessment in brain tumors and recently has shown promise in tumors in the bones, breast, prostate, and other tissues.29 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis has been linked to MRI contrast agents that contain gadolinium.30 This condition has been described in patients with substantially impaired renal function who receive MRI contrast material intravenously. “Black box” warning labels now appear on the product inserts for MRI, and we are seeing increased use of alternative imaging methods to MRI in patients with low creatinine clearance rates followed by sequential imaging studies. Gadolinium may be responsible in part for this process because it has been found in the skin of some of such affected patients.31,32 In 2007, black box warning labels were added to the package inserts related to MRI contrast material containing gadolinium (Box 18-2). An exciting area of application of MRI technology is in the field of whole-body MRI. Such a test may begin to offer whole-body cancer surveys with no ionizing radiation delivered to the patient. Such applications to date have been less sensitive than whole-body PET imaging, but this area is emerging very rapidly33 (Figs. 18-2 and 18-3). With positron emitters, the most commonly used tracer is fluorine-18, which is used as the radiolabel for FDG, an agent that images glycolysis in vivo. Because tumors have increased glycolytic metabolism in general, use of this agent in tumor imaging is increasing very rapidly, especially in lung and colorectal tumors and lymphomas.34 In the past several years, combined PET-MRI devices have also been constructed. These devices can include a PET scanner housed within an MRI scanner that perform both PET and MRI studies at the same time, or adjacent PET and MRI scanners that involve precise alignment of the patient table to allow for sequential imaging using PET and then MRI imaging with preservation of patient alignment. PET-MRI is in evolution; two current limitations are the cost of the systems and challenges associated with precise quantitation of the PET images for radioactivity concentrations in vivo because of the limitations intrinsic to MRI-based attenuation correction algorithms.35 Higher doses of radioactive isotopes also can be therapeutic. For example, iodine-131 is used for the treatment of thyroid cancer, as sodium iodide. The same isotope, conjugated to an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has been approved by the U.S. FDA to treat low-grade and transformed B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is considered refractory to standard treatments. The tracer doses are used to guide the treatment doses in such instances or at least to determine if the radioantibody has any unexpected targeting behavior.36 The possibility of constructing light-emitting contrast media is a real one, and optical imaging has the potential to provide remarkable sensitivity and resolution in superficial structures. However, it is not routinely applied in cancer imaging, with the exception of visualization of the interior of the eye, visualization of the cervix, and endoscopy from above and below.37 The combination of light-generating acoustic signals, that is, photoacoustic imaging, also has considerable promise and potential for areas of the body in which light can be delivered at sufficient intensity. The strengths and weaknesses of the major imaging methods are contrasted in Table 18-1. Table 18-1
Imaging
Introduction
General Considerations
Performance of Imaging Tests
Sensitivity
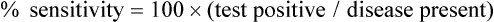
Specificity
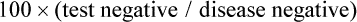
Positive and Negative Predictive Values
Receiver Operator Characteristic Curves
Other Approaches to Assessing the Value of Imaging
Screening Concepts and Challenges
Screening Costs
Size of Detectable Lesions
Major Imaging Modalities
Plain Film Radiographs
Mammography
Computed Tomography
Angiography
Ultrasound
MRI and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
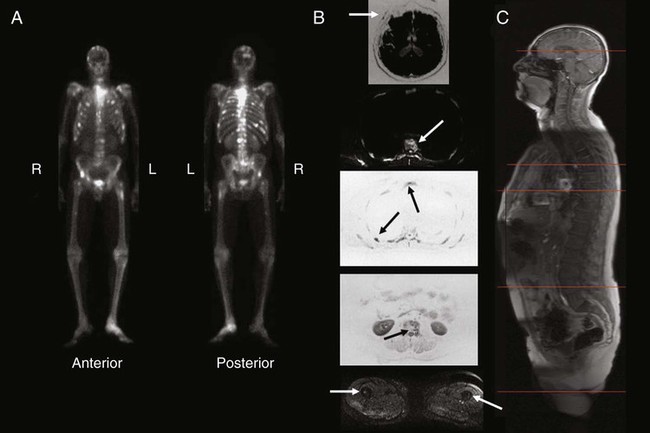
Nuclear Medicine and PET
Optical Imaging Methods
Modality
Resolution
Sensitivity
Specificity
Functional Imaging Ability
Magnetic resonance imaging
1-2 mm
Moderate
Moderate
Moderate with spectroscopy ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access