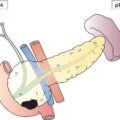
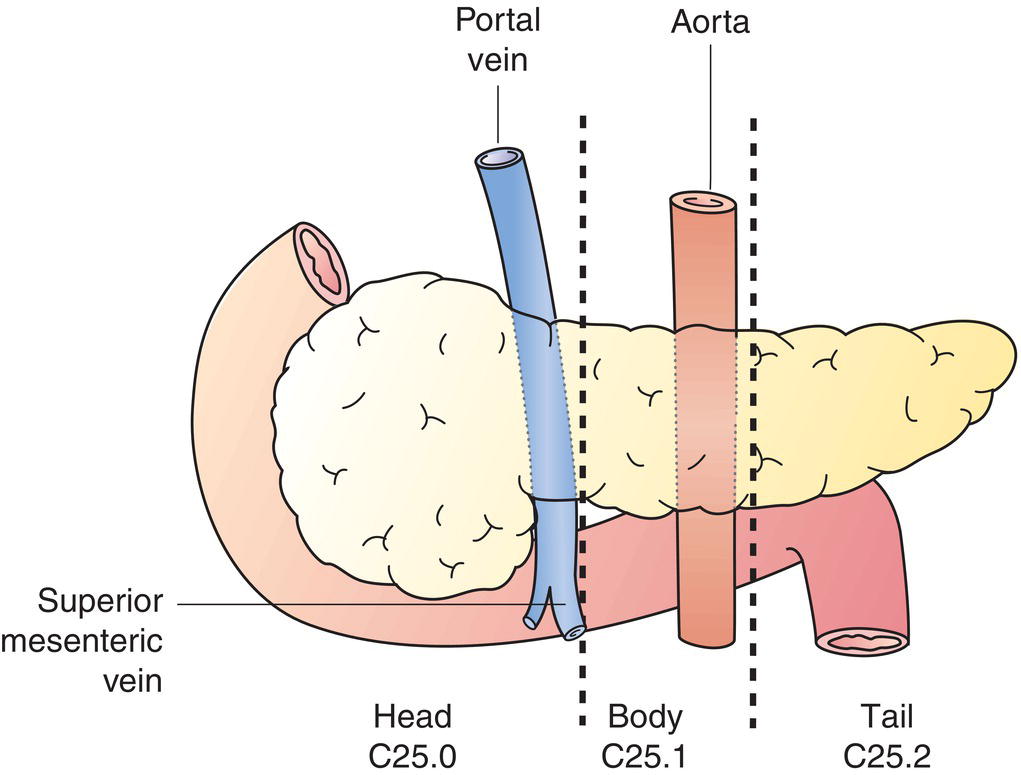
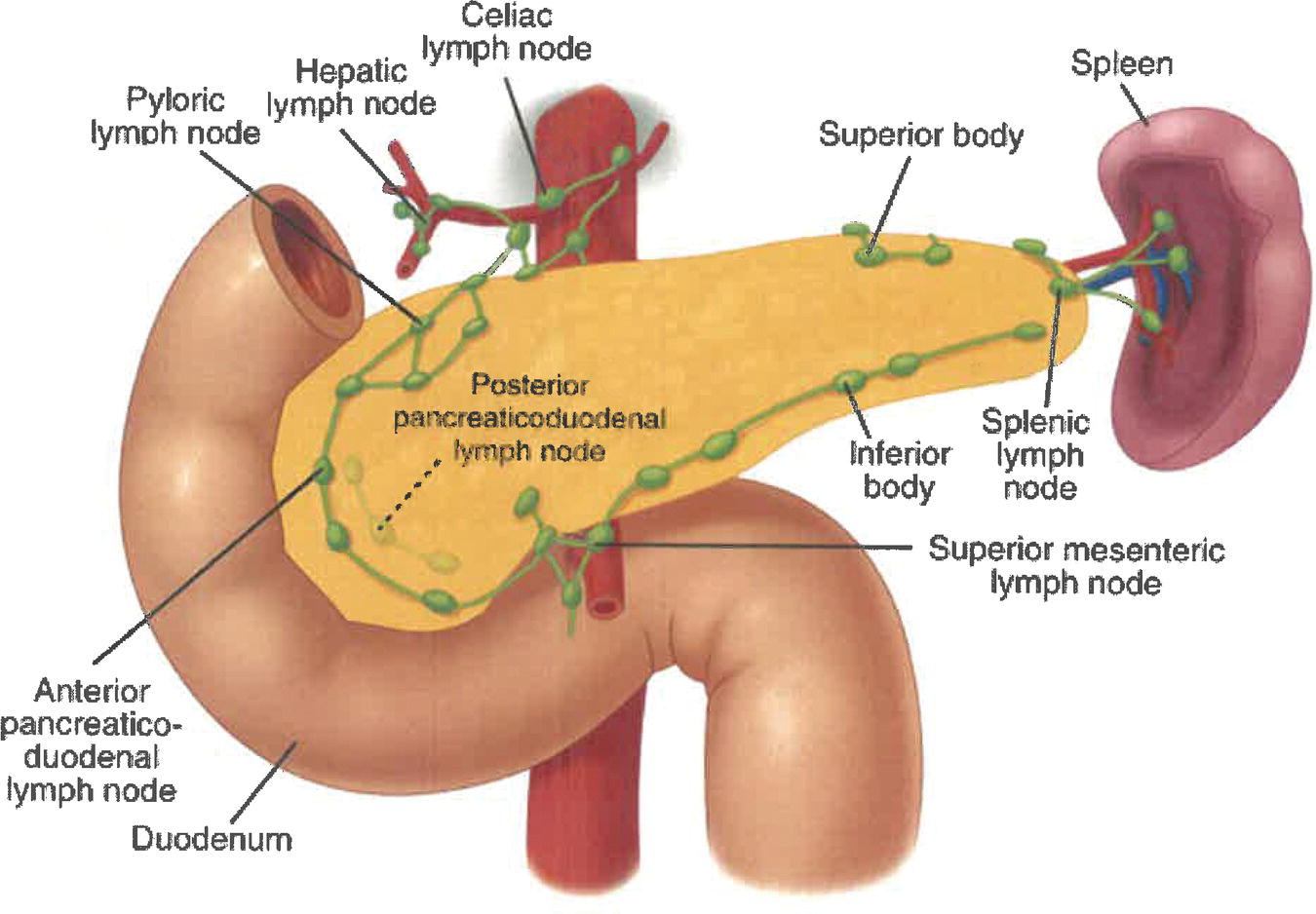
The classification applies to carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, including carcinoids. There should be histological or cytological confirmation of the disease. Notes 1 Tumours of the head of the pancreas are those arising to the right of the left border of the superior mesenteric vein. The uncinate process is considered as part of the head. 2 Tumours of the body are those arising between the left border of the superior mesenteric vein and the left border of the aorta. 3 Tumours of the tail are those arising between the left border of the aorta and the hilum of the spleen. Source: From F. Charles Brunicardi et al., Schwartz’s Principles of Surgery, 10th edition, 2015, McGraw Hill Education. © 2015 McGraw Hill Education The regional lymph nodes for tumours in the head and neck of the pancreas are the lymph nodes along the anterior and posterior pancreaticoduodenal vessels, the superior mesenteric vein and right lateral wall of the superior mesenteric artery, proximal mesenteric vessels, the common hepatic artery, coeliac axis, pyloric, infrapyloric, subpyloric vessels, portal vein and common bile duct (not shown). The regional lymph nodes for tumours in body and tail are the lymph nodes along the common hepatic artery, coeliac axis, splenic artery and splenic hilum, as well as retroperitoneal nodes and lateral aortic nodes. Note * Tis also includes the “PanIN‐III” classification. The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
PANCREAS (ICD‐O‐3 C25)
Rules for Classification
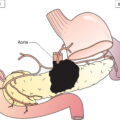
Anatomical Subsites (Fig. 238)
C25.0
Head of pancreas
C25.1
Body of pancreas
C25.2
Tail of pancreas
C25.3
Pancreatic duct
C25.4
Islets of Langerhans (endocrine pancreas)
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 239)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis
Carcinoma in situ*
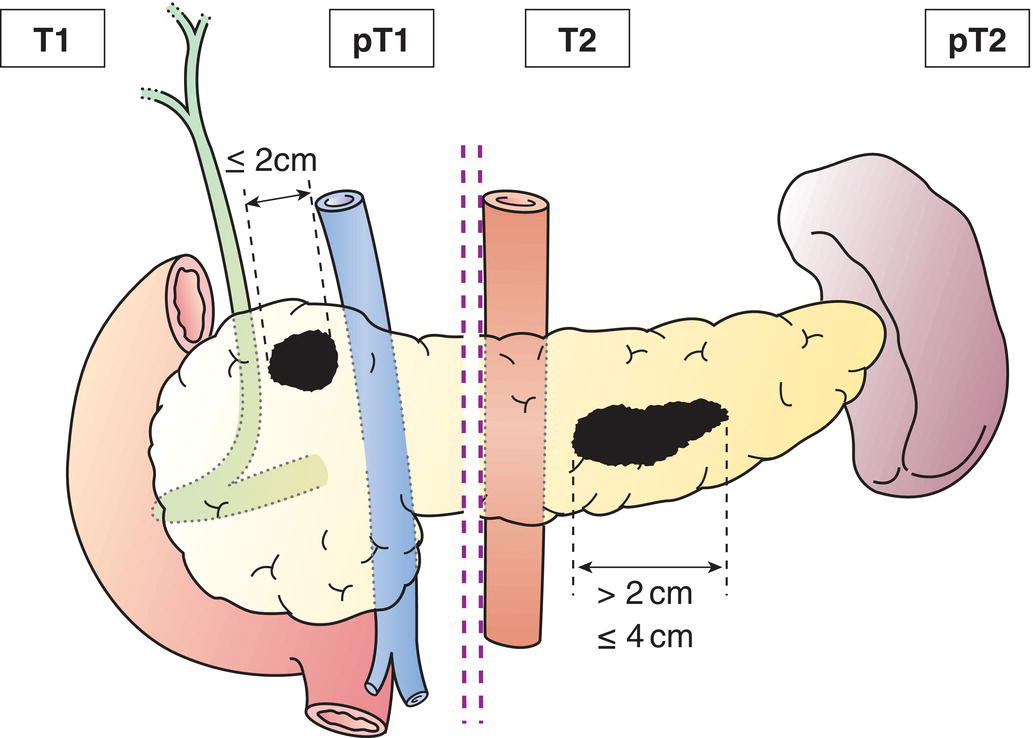
T1
Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension (Fig. 240)
T1a
Tumour 0.5 cm or less in greatest dimension
T1b
Tumour greater than 0.5 cm and no more than 1 cm in greatest dimension
T1c
Tumour greater than 1 cm but no more than 2 cm in greatest dimension
T2
Tumour limited to pancreas, more than 2 cm but no more than 4 cm in greatest dimension (Fig. 240)
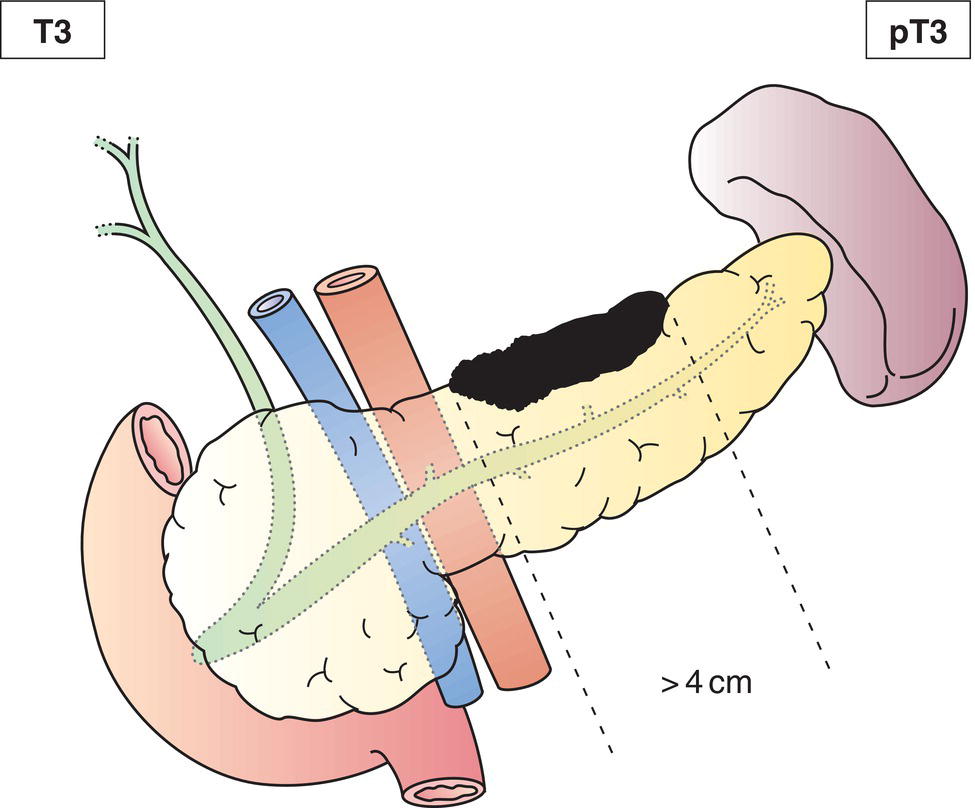
T3
Tumour limited to pancreas, more than 4 cm in greatest dimension (Fig. 241)
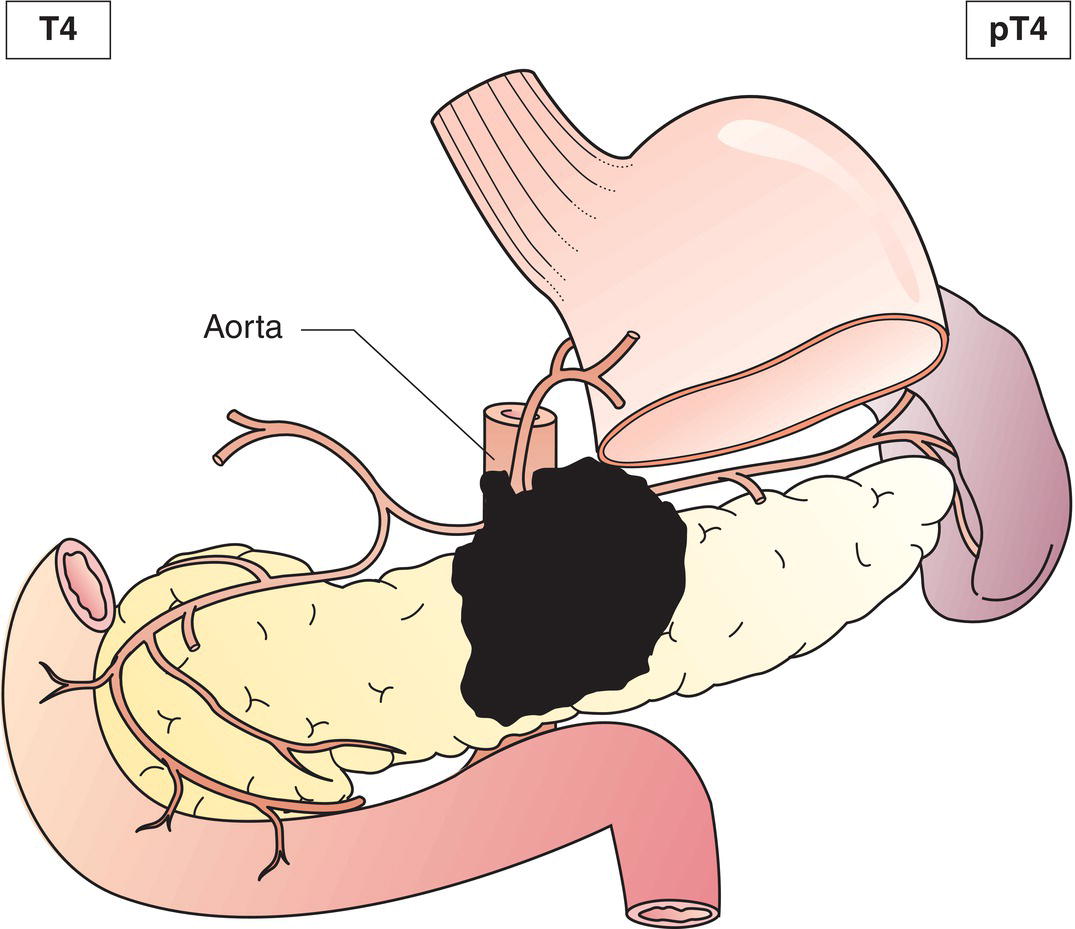
T4
Tumour involves coeliac axis, superior mesenteric artery and/or common hepatic artery (Fig. 242)
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
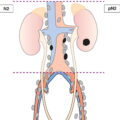
N1
Metastases in 1 to 3 regional lymph node(s) (Fig. 243)
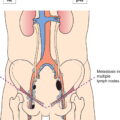
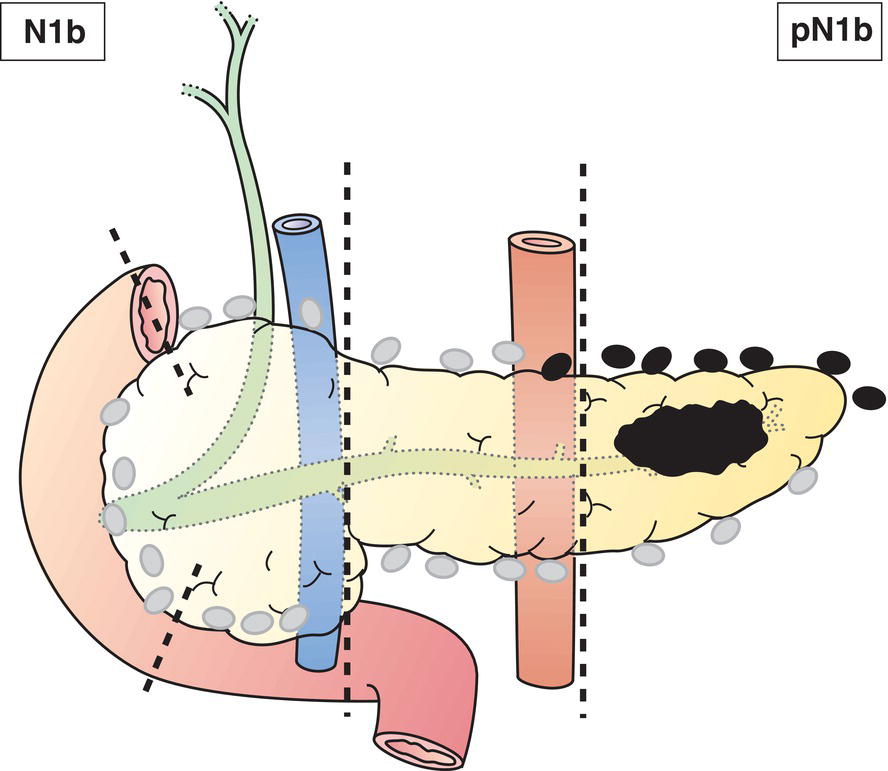
N2
Metastases in 4 or more regional lymph nodes (Fig. 244) 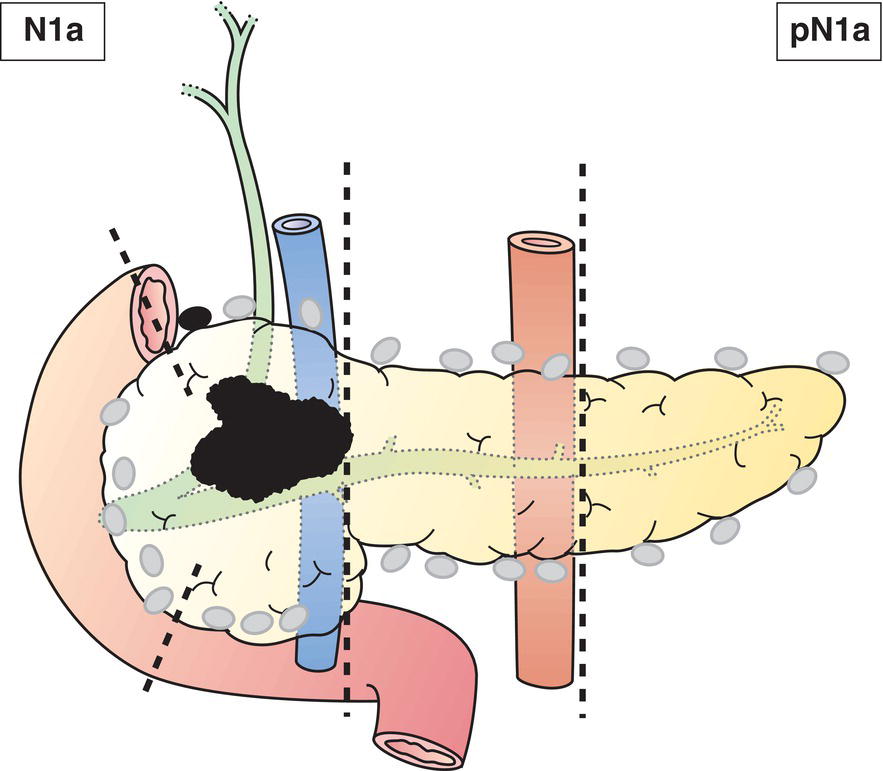
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
TNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pN0
Histological examination of a regional lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 12 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree