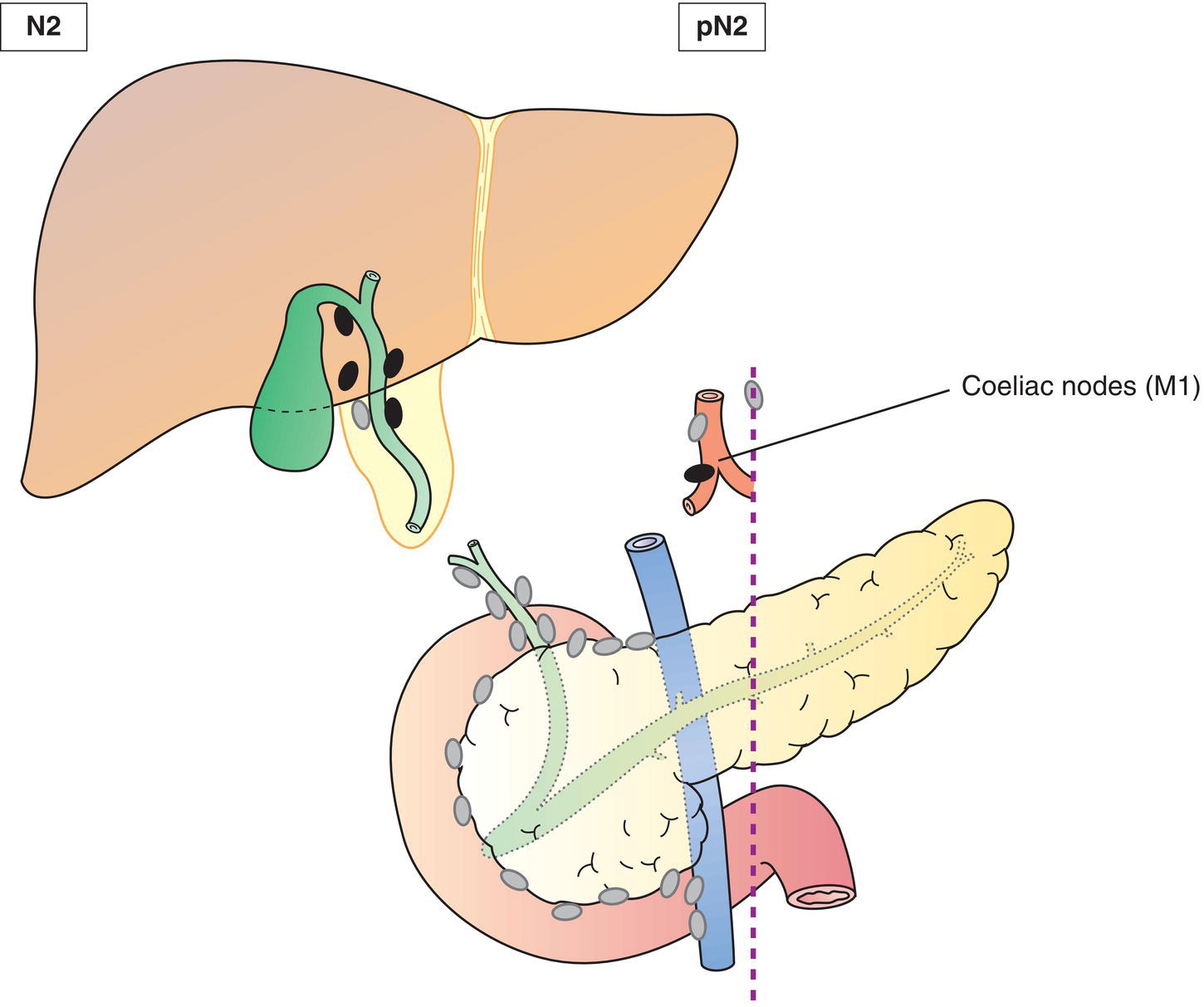
The classification applies only to carcinomas of the gallbladder and cystic duct. There should be histological confirmation of the disease. Regional lymph nodes are limited to the hepatic hilus (including nodes along the common bile duct, hepatic artery, portal vein and cystic duct). Coeliac, periduodenal, peripancreatic and superior mesenteric artery node involvement is considered distant metastasis (M1). The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
GALLBLADDER (ICD‐O‐3 C23.9 and C24.0)
Rules for Classification
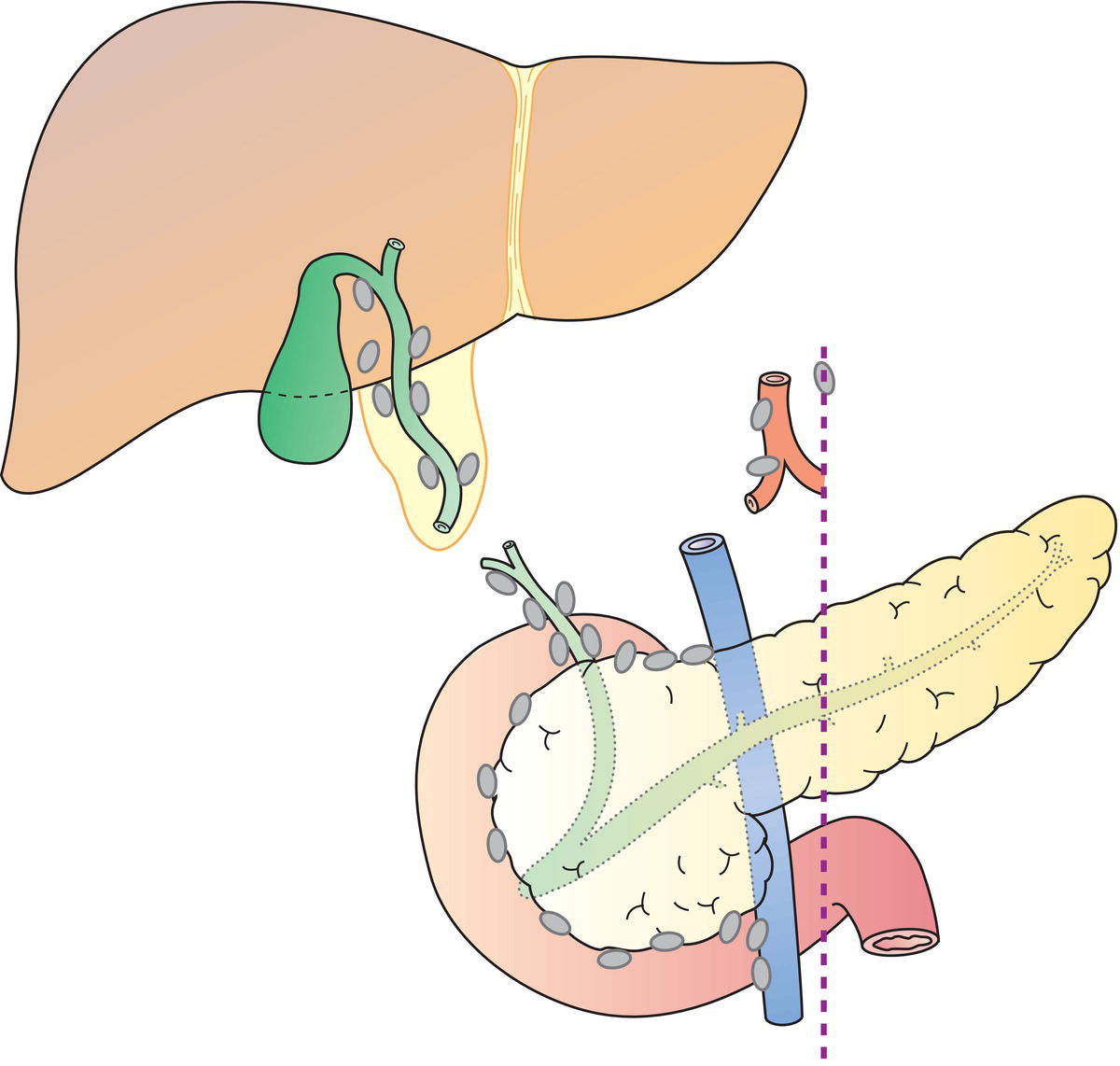
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 216)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis
Carcinoma in situ
T1
Tumour invades lamina propria or muscular layer (Fig. 213)
T1a
Tumour invades lamina propria
T1b
Tumour invades muscular layer
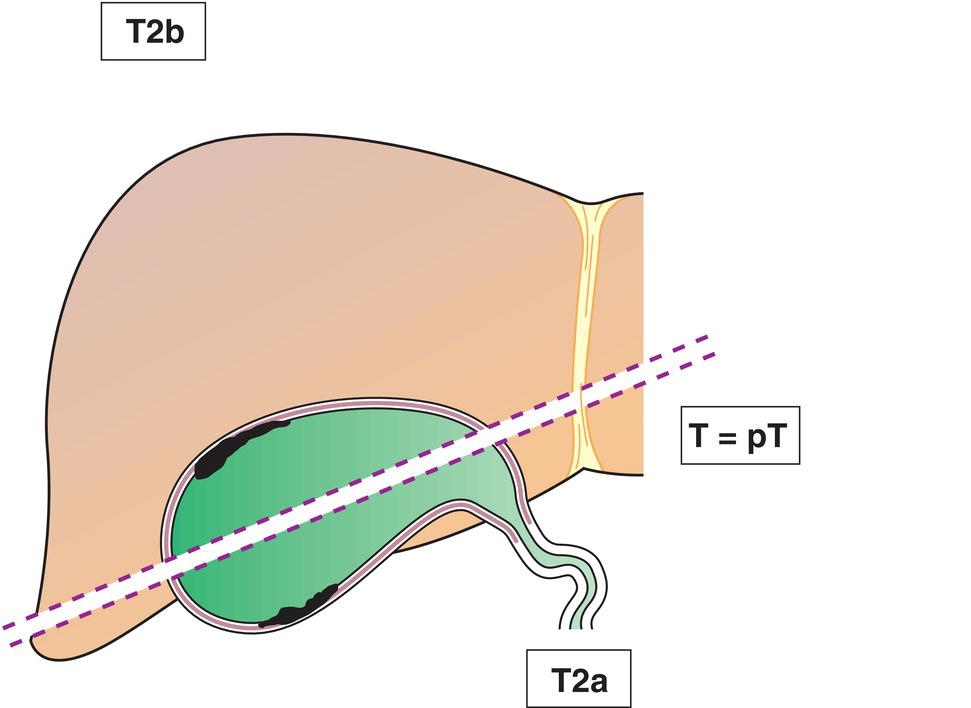
T2
Tumour invades perimuscular connective tissue; no extension beyond serosa or into liver (Fig. 214)
T2a
Tumour invades perimuscular connective tissue on the peritoneal side with no extension to the serosa
T2b
Tumour invades perimuscular connective tissue on the hepatic side with no extension into the liver
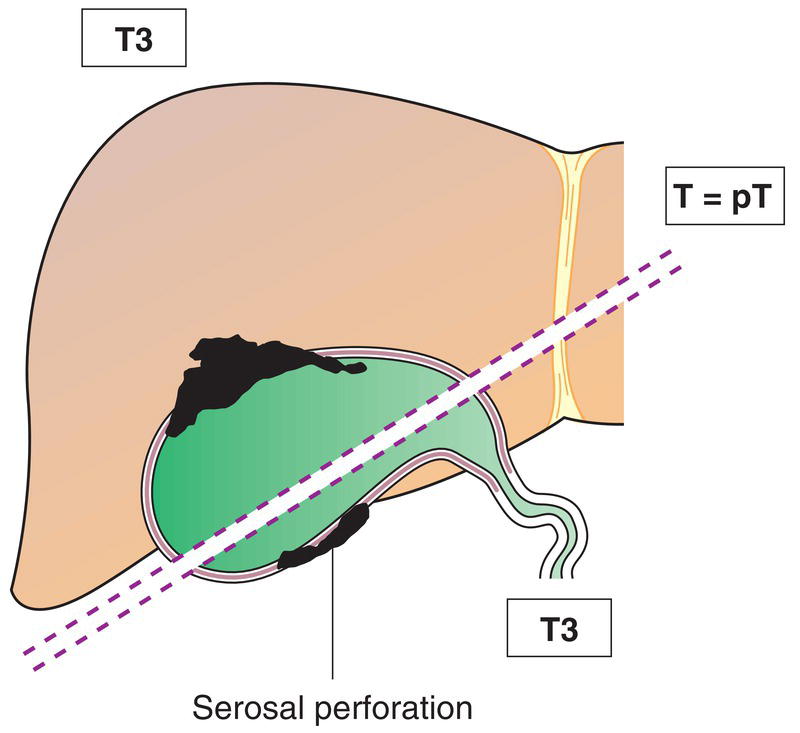
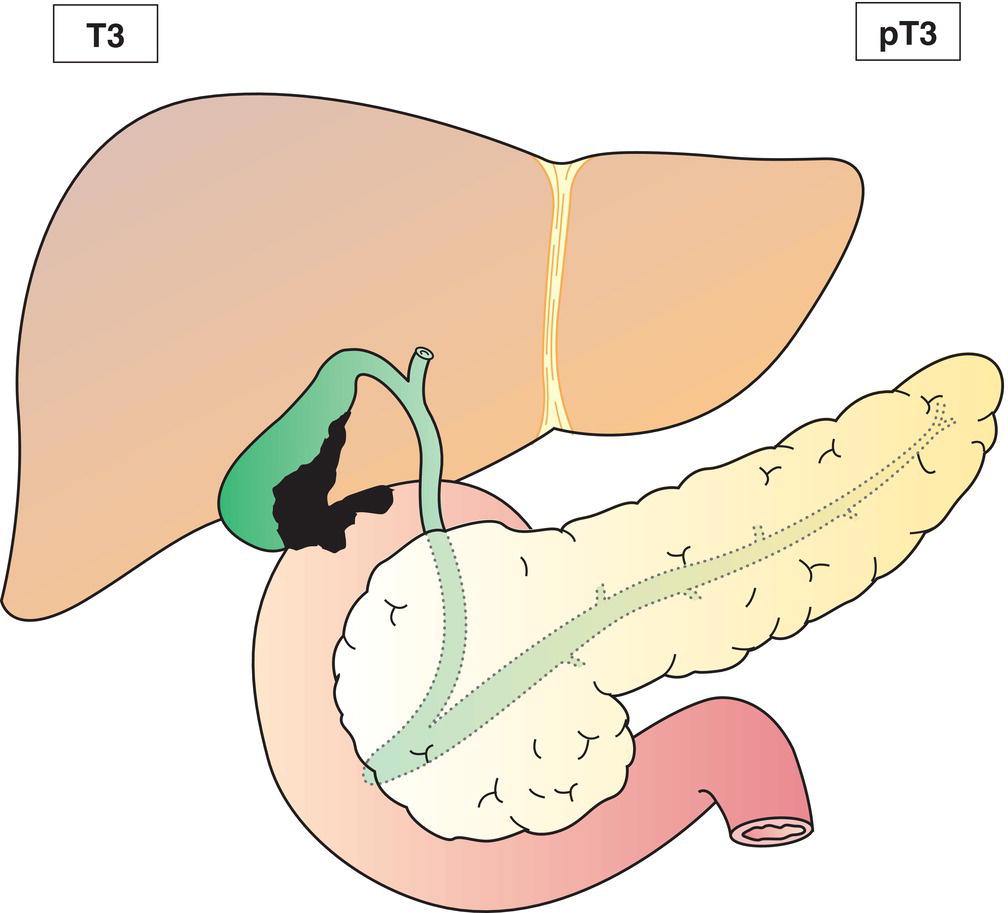
T3
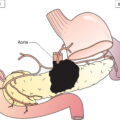
Tumour perforates the serosa (visceral peritoneum) and/or directly invades the liver and/or one other adjacent organ or structure, such as stomach, duodenum, colon, pancreas, omentum, extrahepatic bile ducts (Figs. 215, 216)
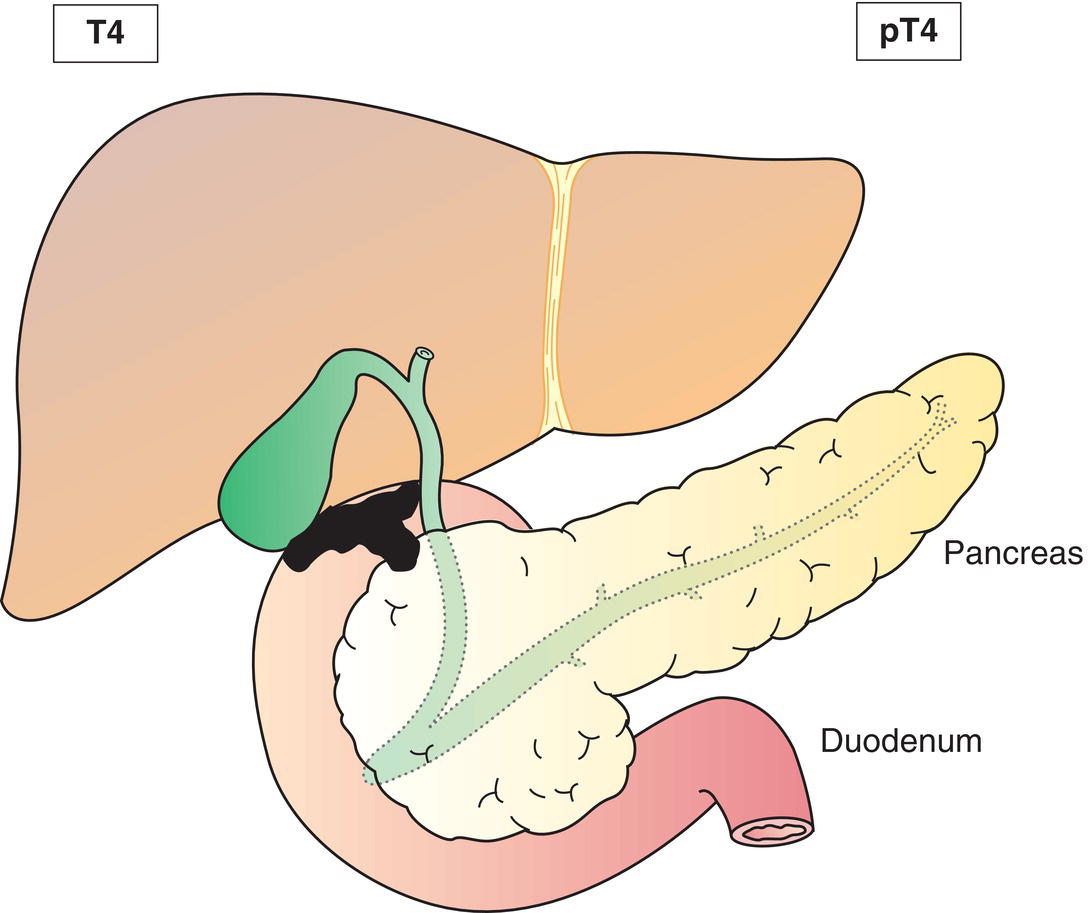
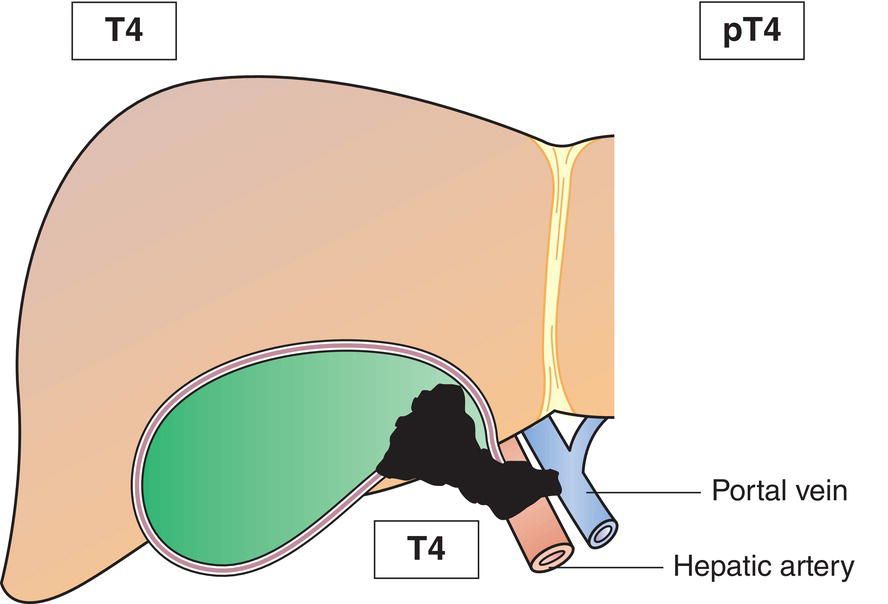
T4
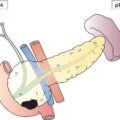
Tumour invades main portal vein or hepatic artery or invades two or more extrahepatic organs or structures (Figs. 217, 218) 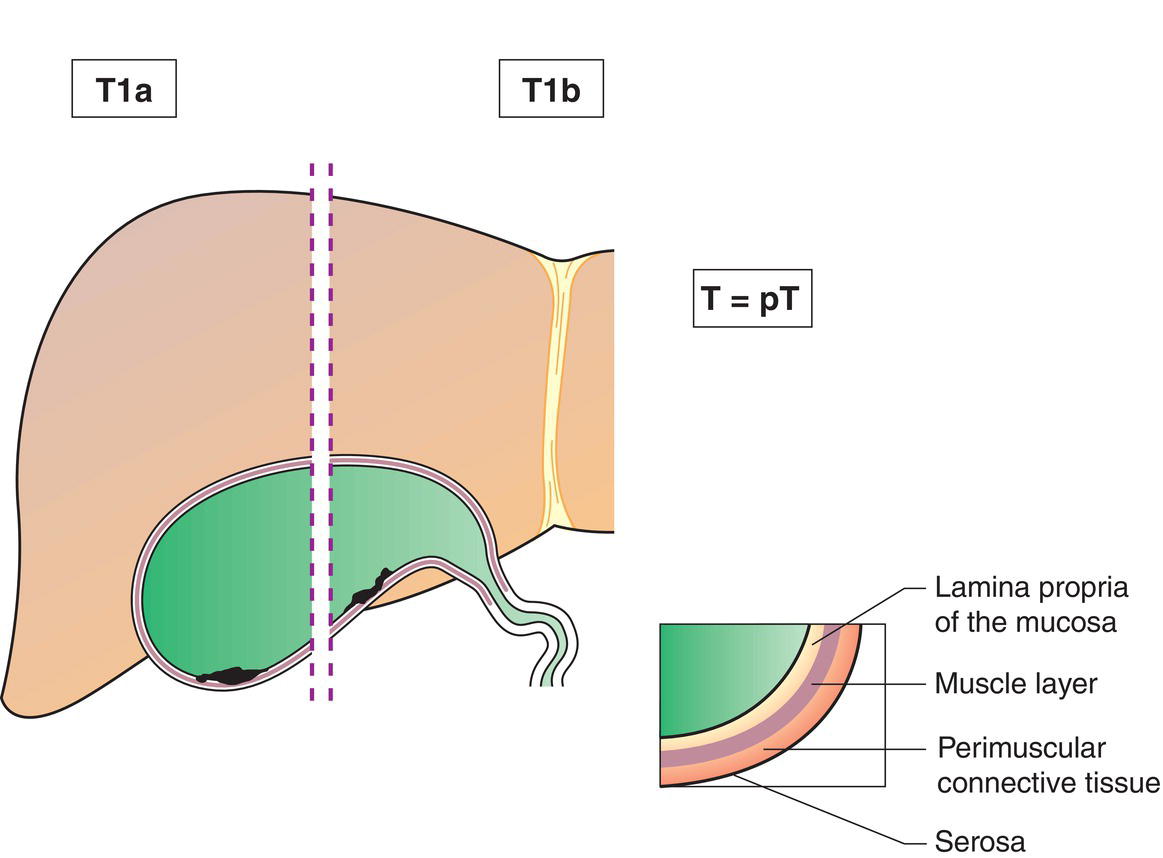
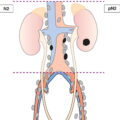
N – Regional Lymph Nodes (Figs. 219, 220)
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
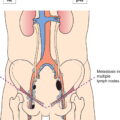
N1N2
Metastases to 1‐3 nodesMetastases to 4 or more nodes 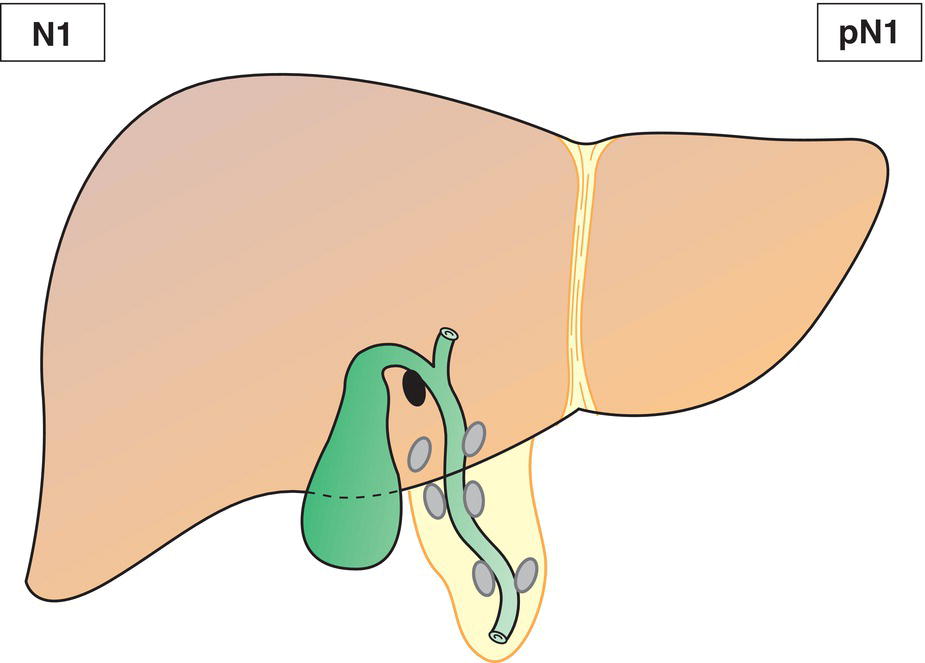
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
TNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pN0
Histological examination of a regional lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 3 or more lymph nodes. If the regional lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree