Definition: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of a nation’s economic output and is defined as the total monetary value of all goods and services produced by a country in one year. The top map shows GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power. The GDP per capita is simply the GDP divided by the number of people in the country. Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a method for adjusting for differences in the price of everyday items between countries by adjusting the GDP for the relative cost in US dollars of a common ‘basket of goods.’
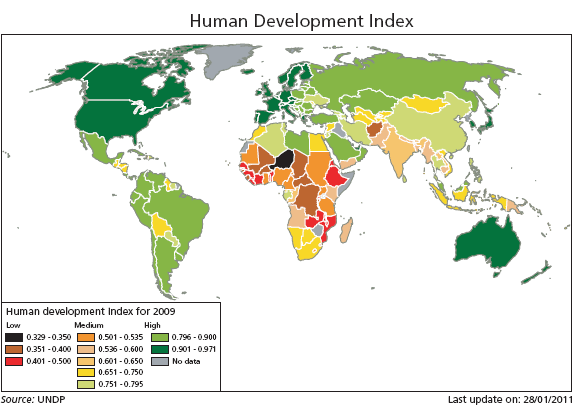
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite measure developed by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) and introduced in 1990 to provide a single metric for comparing the level of socioeconomic development of countries. It is a derived from measures of life expectancy at birth, GDP per capita, and educational attainment. HDI is expressed as a value from 0 (lowest) to 1 (highest).
Trends: Economic development is a global phenomenon, and between 1999 and 2005 the number of people living on $1.25 per day or less fell by 325 million. The speed of development has not, however, been equal and Sub-Saharan Africa has lagged behind other regions. Following independence from colonial rule in the mid 1970s, Sub-Saharan Africa has been characterized by low growth with a long period of stagnation, and even declines in GDP, between the 1970s and mid-1990s; but from around 1995 growth has taken off.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




