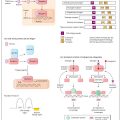
Table 6.1 Relative potency of some synthetic GnRH agonists
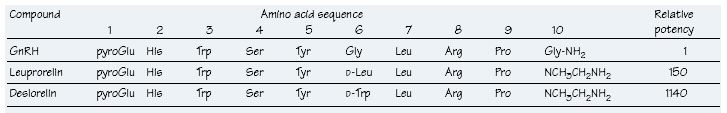
D-signifies the D-isomer of the amino acid
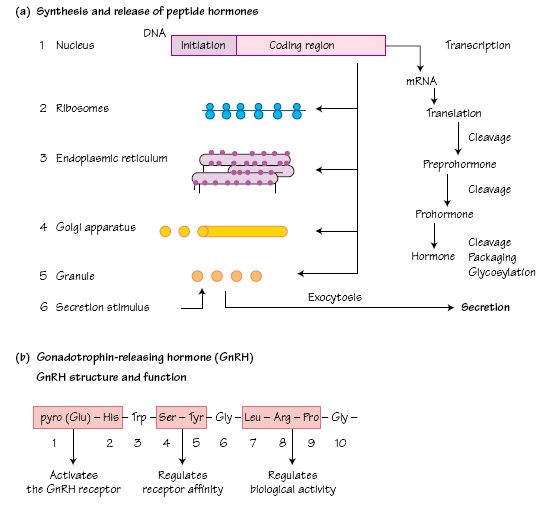
The therapeutic use of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and its analogues is based on the discovery that pulsatile exposure of gonadotrophs to GnRH is required to maintain normal anterior pituitary function, whereas continuous GnRH secretion results in desensitization of the gonadotrophs and suppression of LH and FSH release. Thus GnRH or its analogues can be used in a pulsatile fashion to promote fertility in women with isolated GnRH deficiency or given continuously to suppress sex hormone secretion in patients with hormone- related cancers. Stable synthetic analogues of GnRH have been developed since GnRH, although used therapeutically as gonadorelin to assess pituitary function, is unstable and not satisfactory as a therapeutic agent. Stable analogues, including buserelin, goserelin, leuprorede, deslorelin and nafarelin, may be used to treat breast and prostate cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids and infertility.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree