Fig. 15.1
(a) Human pancreatic-cancer-patient tumor with RFP and GFP stromal cells. Image was obtained with the Olympus FV1000. Green arrows indicate GFP stromal cells from GFP mouse. Red arrows indicate RFP stromal cells from RFP mouse. (Bar=50 μm). (b) Human pancreatic-cancer-patient tumor with RFP stromal cells and GFP TAMs. (Bar=100 μm). Image taken with the Olympus FV1000. (c) High magnification image of (b). RFP stromal cells and GFP-TAMs are readily observed. (Bar=30 μm). Image obtained with the Olympus FV1000 [34]
GFP Host Stromal Cells Infiltrate Peritoneal Disseminated Metastases of Pancreatic Cancer PDOX
The GFP stromal cells from the GFP host mouse formed a capsule around the disseminated peritoneal metastases. Both GFP-labeled CAFs and TAMs were observed in the disseminated peritoneal metastases. Histological examination at 110 days of tumor growth demonstrated pancreatic tubular adenocarcinoma, similar to the primary tumor [26].
GFP Host Stromal Cells Infiltrate Liver Metastases of Pancreatic Cancer PDOX
High-magnification fluorescence imaging showed extensive GFP fluorescence in the liver metastasis. Both GFP CAFs and TAMs were observed in the liver metastasis. Histological examination of the liver metastasis demonstrated pancreatic tubular adenocarcinoma [26].
RFP Host Stromal Cells Infiltrate Pancreatic Cancer PDOX
Patient pancreatic cancer was transplanted orthotopically in 6-week-old transgenic RFP nude mice. After 30 days, tumors were imaged using the OV100. The RFP stromal cells from the RFP host mice formed a capsule around the tumor and infiltrated into the central part of the tumor as well. RFP-expressing TAMs could be visualized in the tumor [34].
GFP Host Stromal Cells Infiltrate Pancreatic PDOX Labeled with RFP Stroma to Form a Two-Color Stroma Model
Tumors were grown in RFP transgenic nude mice and subsequently in GFP nude mice, after which the human pancreatic-cancer PDOX contained both RFP and GFP stromal cells. The RFP stromal cells still persisted after passage to GFP transgenic mice. Under confocal microscopy with the FV1000, RFP and GFP stromal cells were clearly visualized in the tumor including GFP and RFP CAFs and TAMs in the central part of the tumor [34].
CFP Host Stromal Cells Infiltrate Pancreatic Cancer PDOX Previously Grown in RFP and GFP Transgenic Nude Mice to Form a Three-Color Stroma Model
Pancreatic cancer previously grown in RFP and GFP transgenic mice were orthotopically implanted in 6-week-old nude CFP mice. The tumors were excised and observed with the FV1000 confocal microscope. RFP-, GFP-, and CFP-expressing stromal cells were observed in the human pancreatic-cancer patient tumor. The RFP stroma persisted after two passages and GFP stroma persisted after one passage in CFP mice. RFP TAMs and CAFs and GFP blood vessels still persisted in the human pancreatic-cancer patient tumor after one and two passages, respectively [34] (Fig. 15.2).
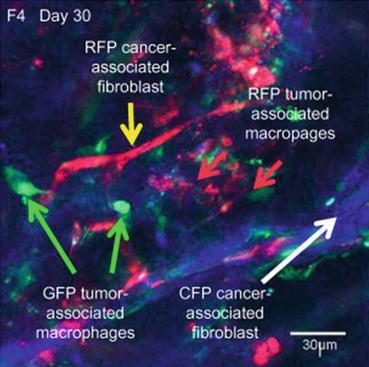

Fig. 15.2
Human pancreatic-cancer-patient PDOX tumor growing in CFP nude-mouse-host after previous growth in RFP and GFP nude-mouse-hosts. RFP CAFs (yellow arrow) and GFP TAMs (green arrows) in the PDOX tumor. White arrow indicates CFP CAFs. (Bar=30 μm). Image was obtained with the FV1000 confocal microscope [34]
OBP-401-GFP Labeling of Cancer Cells in Pancreatic Cancer PDOX with RFP-Expressing Stroma
OBP-401 selectively labeled cancer cells with GFP in the pancreatic cancer PDOX containing RFP-expressing stroma obtained from previous growth in RFP transgenic nude mice. The double-labeled PDOX enabled precise visualization of color-coded cancer and stromal cells [26] (Fig. 15.3).
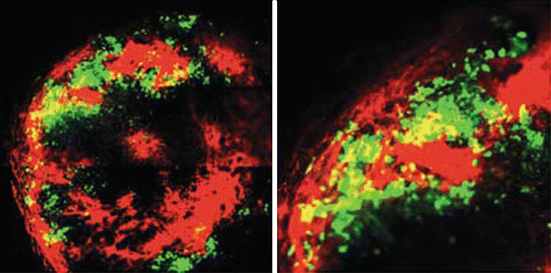

Fig. 15.3
FGS of a pancreatic cancer PDOX with GFP-labeled cancer cells and RFP-labeled stroma. RFP-stroma were acquired by previous growth of the PDOX in RFP transgenic nude mice. GFP-cancer cells were obtained from infection with OBP-401-GFP. Representative images of a cross-section of the resected dual-color tumor. Images were acquired with the FV1000 confocal laser imaging system [26]
Noninvasive Imaging of Pancreatic Cancer PDOX with Labeled Stromal Cells
Noninvasive imaging at days 21, 30, and 74 demonstrated extensive orthotopic growth of the pancreatic cancer PDOX, labeled with RFP and GFP stroma, on the nude mouse pancreas [21] (Fig. 15.4).
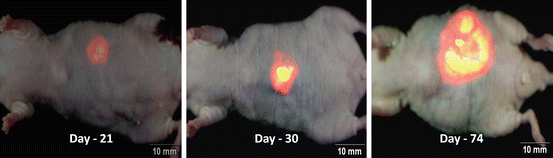

Fig. 15.4
Non-invasive imaging of fluorescent tumor from a patient with pancreatic cancer growing in a PDOX model in non-transgenic nude mice. The PDOX was previously grown in transgenic RFP and transgenic GFP nude mice where the PDOX acquired RFP and GFP stroma, respectively. Whole-body non-invasive imaging with the OV100 of human pancreatic cancer PDOX in non-transgenic nude mice. Mice were non-invasively imaged at day-21 (left panel), day-30 (middle panel) and day-74 (right panel) [21]
Noninvasive Imaging of a PDOX Sarcoma in Non-colored Nude Mouse After a Single Passage in RFP Nude Mice
A patient soft tissue sarcoma (STS) was grown orthotopically in the right biceps femoris of an RFP-expressing nude mouse. The PDOX tumor in the RFP-expressing nude mouse became brightly fluorescent. The resected PDOX tumor from the RFP transgenic nude mouse was also brightly fluorescent. The RFP-expressing PDOX tumor was passaged orthotopically to the right biceps femoris of non-fluorescent nude mice to establish a noninvasively imageable PDOX model. The bright RFP-expressing STS PDOX was readily visible without opening the skin. The STS PDOX tumor in the nontransgenic nude mouse was then exposed by a skin flap. Tumor RFP expression was very bright when imaged through the skin flap. The resected RFP-expressing PDOX was also very bright [27].
FV1000 confocal laser microscopy imaging visualized RFP-expressing tumor stroma in the STS PDOX derived from RFP-expressing nude mice, after passage to a nontransgenic nude mouse. The PDOX tumors had bright and diffusely distributed RFP-expressing stroma with fibroblast-like cells and lymphocyte-like cells [27].
The results in this chapter demonstrate the feasibility of labeling PDOX mouse models with fluorescent proteins. Cancer cells as well as stroma can be differentially labeled. The color-coded tumor stroma model is a powerful measure to simultaneously visualize the two types of cells within the PDOX tumors and how they may differentially respond to approved and experimental therapeutics agents. In addition, the stroma acquired by the PDOX appears stable and able to grow in parallel with the cancer cells of the PDOX. The labeling with adenovirus OBP-401-GFP also appears stable.
References
1.
Fu X, Besterman JM, Monosov A, Hoffman RM. Models of human metastatic colon cancer in nude mice orthotopically constructed by using histologically intact patient specimens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:9345–9.CrossrefPubMedPubMedCentral
2.
Fu X, Guadagni F, Hoffman RM. A metastatic nude-mouse model of human pancreatic cancer constructed orthotopically from histologically intact patient specimens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:5645–9.CrossrefPubMedPubMedCentral
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree