F
famciclovir
Chemical Class: Acyclic purine nucleoside analog
| Creatinine Clearance | Herpes Zoster | Genital Herpes |
|---|---|---|
| 40-59 ml/min | 500 mg q12h | 125 mg q12h |
| 20-39 ml/min | 500 mg q24h | 125 mg q24h |
| less than 20 ml/min | 250 mg q24h | 125 mg q24h |
 Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to penciclovir cream
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to penciclovir cream
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
famotidine
 Brand Name(s): Pepcid, Pepcid RPD
Brand Name(s): Pepcid, Pepcid RPD
OTC: with calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide (Pepcid Complete)
Chemical Class: Thiazole derivative
Acute treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers: PO 40 mg/day at bedtime.
Duodenal ulcer maintenance: PO 20 mg/day at bedtime.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease: PO 20 mg twice a day.
Esophagitis: PO 2-40 mg twice a day.
Hypersecretory conditions: PO Initially, 20 mg q6h. May increase up to 160 mg q6h.
Usual parenteral dosage: IV 20 mg q12h.
Dosage in renal impairment: Dosing frequency is modified based on creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosing Frequency |
|---|---|
| 10-50 ml/min | q24h |
| less than 10 ml/min | q36-48h |
 Unlabeled Uses: Autism, prevention of aspiration pneumonitis, Helicobacter pylori eradication
Unlabeled Uses: Autism, prevention of aspiration pneumonitis, Helicobacter pylori eradication
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Cognitive impairment
Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Cognitive impairment
1 Gawrich S, Shaker R. Medical management of nocturnal symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in the elderly. Drugs Aging. 2003;20:509-516.
2 Thomson ABR. Gastro-oesophageal reflux in the elderly. Role of drug therapy in management. Drugs Aging. 2001;18:409-414.
3 Drugs that may cause cognitive disorders in the elderly. Med Lett. 2000;42:111-112.
felodipine
Chemical Class: Dihydropyridine
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of CHF, chronic angina pectoris, Raynaud’s phenomenon
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of CHF, chronic angina pectoris, Raynaud’s phenomenon
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
fenofibrate
 Brand Name(s): Antara, Lipidil Supra, Lofibra, Tricor, Triglide
Brand Name(s): Antara, Lipidil Supra, Lofibra, Tricor, Triglide
Chemical Class: Fibric acid derivative
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
fenoldopam mesylate
(fhe-knowl’-doh-pam mes’-sil-ate)
Chemical Class: Benzazepine derivative
 Unlabeled Uses: Prevention of contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity
Unlabeled Uses: Prevention of contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity
 Contraindications: Sensitivity to sulfites
Contraindications: Sensitivity to sulfites
Special Considerations
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
fenoprofen calcium
(fen-oh-proe’-fen kal’-see-um)
Chemical Class: Propionic acid derivative
Mild to moderate pain: PO 200 mg q4-6h as needed.
Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis: PO 300-600 mg 3-4 times a day.
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, vascular headaches
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, vascular headaches
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 Brand Name(s): Famvir
Brand Name(s): Famvir Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
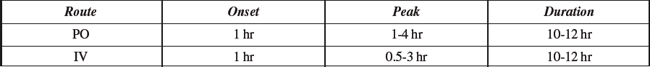
 Available Forms:
Available Forms: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Acute allergic reactions, urticaria (in addition to antihistamine therapy)
Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Acute allergic reactions, urticaria (in addition to antihistamine therapy) Side Effects:
Side Effects: Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Adjust dose based on creatinine clearance. Not effective in preventing NSAID-induced gastric ulceration and bleeding; proton pump inhibitors should be used for this indication instead.
Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Adjust dose based on creatinine clearance. Not effective in preventing NSAID-induced gastric ulceration and bleeding; proton pump inhibitors should be used for this indication instead. Brand Name(s): Plendil
Brand Name(s): Plendil
 Available Forms:
Available Forms: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Available Forms:
Available Forms: Contraindications: Gallbladder disease, severe renal or hepatic dysfunction (including primary biliary cirrhosis, unexplained persistent liver function abnormality)
Contraindications: Gallbladder disease, severe renal or hepatic dysfunction (including primary biliary cirrhosis, unexplained persistent liver function abnormality) Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Brand Name(s): Corlopam
Brand Name(s): Corlopam Available Forms:
Available Forms: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Brand Name(s): Nalfon
Brand Name(s): Nalfon Available Forms:
Available Forms: Contraindications: Active peptic ulcer disease, chronic inflammation of GI tract, GI bleeding or ulceration, history of hypersensitivity to aspirin or NSAIDs, significant renal impairment
Contraindications: Active peptic ulcer disease, chronic inflammation of GI tract, GI bleeding or ulceration, history of hypersensitivity to aspirin or NSAIDs, significant renal impairment Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions

 Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Hepatic impairment, CHF, HTN, PUD, History of GI bleeding, GERD, Bleeding and platelet disorders, History of aspirin sensitivity reaction. Also use with caution in patients taking Anticoagulants, Aspirin, and Antihypertensive agents.
Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Hepatic impairment, CHF, HTN, PUD, History of GI bleeding, GERD, Bleeding and platelet disorders, History of aspirin sensitivity reaction. Also use with caution in patients taking Anticoagulants, Aspirin, and Antihypertensive agents. U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations

 Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Acute Gout
Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Acute Gout Side Effects:
Side Effects: Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Use with caution due to the higher risk of GI adverse events. Not a preferred NSAID in older adults. Use of NSAIDs in older adults increases the risk of GI complications including gastric ulceration, bleeding, and perforation. These complications are not necessarily preceded by less severe GI symptoms. Concomitant use of a proton pump inhibitor or misoprostol reduces the risk for gastric ulceration and bleeding, but may not prevent long-term GI toxicity.
Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Use with caution due to the higher risk of GI adverse events. Not a preferred NSAID in older adults. Use of NSAIDs in older adults increases the risk of GI complications including gastric ulceration, bleeding, and perforation. These complications are not necessarily preceded by less severe GI symptoms. Concomitant use of a proton pump inhibitor or misoprostol reduces the risk for gastric ulceration and bleeding, but may not prevent long-term GI toxicity. Brand Name(s): Injection: Sublimaze
Brand Name(s): Injection: Sublimaze


