Structure
“T” stage
Symptom/signs
Central neck
Strap muscles
T3
Hard fixed thyroid mass
Parathyroids
T3
–
Skin
T4a
Skin ulceration/erythema
RLN and SLN
T4a
Dysphonia or weak fatigable voice, stridor
Trachea and Larynx
T4a
Hemoptysis, stridor, cough
Esophagus
T4a
Dysphagia
Prevertebral fascia
T4b
Neck stiffness
Lateral neck
IJV
T4b
Radiological diagnosis
Carotid
T4b
Radiological diagnosis
Sternocleidomastoid
T4b
Lateral neck mass
Phrenic, X, XI
T4b
Raised hemidiaphragm, dysphonia, stiff shoulder
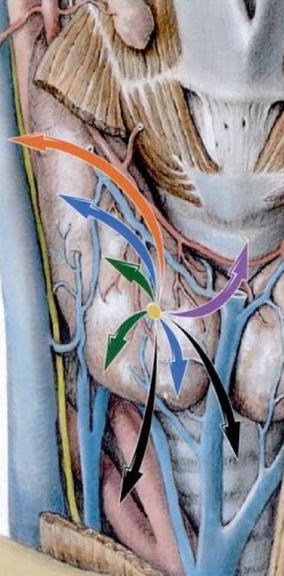
Fig. 24.1
Patterns of thyroid and extra-thyroid extension (green T1, blue T2, purple T3, orange T4a, and black T4b) (Reproduced with permission from Rubin P, Hansen JT. TNM staging atlas. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 91, Fig 12.1)
Investigations
All patients require fiber-optic pharyngolaryngoscopy to examine for intraluminal disease.
CT and MRI with contrast evaluate potential laryngeal cartilage involvement, intraluminal extension, and tracheal, esophageal, and vascular involvement.
The use of iodine contrast in CT delays postoperative radioactive iodine (RAI) scanning for residual or metastatic disease.
Ultrasound is useful for evaluating minimal ETE into strap muscles and has variable reported results for detecting either tracheal or esophageal involvement, 42.9 and 28.6 %, respectively.
Be aware of non-RAI avid tumors (see section “Medical Management”). In this case if the thyroglobulin is high, FDG PET-CT is more likely to show metastatic disease, as these tumors are metabolically active with high glucose uptake.
Barium swallow may show a mucosal esophageal lesion.
Bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy should be undertaken in patients suspected to have ETE to assess mucosal involvement.
Lung function studies may be appropriate in patients with upper aerodigestive tract involvement who may be candidates for partial laryngectomy.
Preoperative speech and swallowing assessments help with intraoperative decision making in terms of recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) resection, partial laryngectomy, and vocal cord augmentation.
Medical Management
By definition all DTC with ETE is treated by adjuvant RAI (ATA 2009 & BTA 2007).
There is no primary role for medical management in medullary thyroid cancer. Patients treated with adjuvant external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) have been shown to have poorer survival though this may reflect the severity of the disease being treated.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree