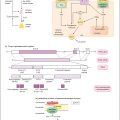
Table 37.1 Causes of endocrine hypertension
| Syndrome | Hormone in excess | Treatment |
| Cushing’s syndrome (pituitary ACTH excess, adrenal cortisol excess, steroid therapy) | Glucocorticoids | Adrenal surgery Pituitary surgery Medical therapy (adrenal blockade) Stop exogenous steroids |
| Conn’s syndrome (adrenal adenoma) Idiopathic hyperaldosteronism (bilateral adrenal hyperplasia) | Aldosterone | Adrenal surgery Medical therapy (spironolactone) |
| Phaeochromocytoma (adrenal medullary tumour) | Catecholamines | Adrenal surgery Medical therapy (α and β blockade) |
| Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism (11β-hydroxylase deficiency) | Aldosterone | Medical therapy (glucocorticoids) |
| Apparent mineralocorticoid excess (11β -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency or suppression by liquorice or carbenoxolone) | Cortisol | Medical therapy (spironolactone) Stop liquorice or carbenoxolone |
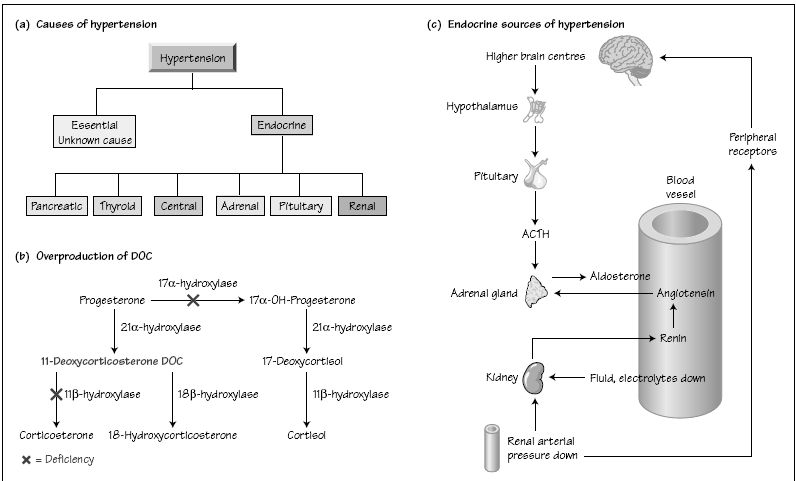
Hypertension affects up to 25% of the population in western countries but only 2–5% will be found to have an identifiable underlying endocrine cause that can be treated. Young people with hypertension should be screened for secondary causes, as should those with a strong family history of hypokalaemia. Treatment is directed towards the underlying cause.
Hypertension may be one of the presenting features of a number of endocrine disorders. Systolic hypertension is typical of thyrotoxicosis, patients with acromegaly are usually hypertensive at presentation and hypertension frequently complicates obesity and diabetes.
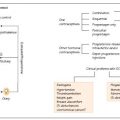
Two main types of hypertension are recognized–the first is essential hypertension, which is the most prevalent type and has no known cause but whose aetiology may involve disturbances of endocrine function, particularly the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (Fig. 37a
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree