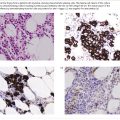
Vessel wall abnormalities
These are associated with easy bruising, purpura and ecchymoses and spontaneous bleeding from mucosal surfaces. Tests of coagulation and platelet function are normal.
Inherited
- Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia is autosomal dominant with multiple dilated microvascular swellings, typically in oropharynx (Fig. 41.1) and gastrointestinal tract, which bleed spontaneously or following minor trauma. Arteriovenous malformations may occur in the lungs or other organs. Local treatment (e.g. nasal packing) may control bleeding; tranexamic acid helps to reduce bleeding. Chronic iron deficiency is frequent.
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome and other rare connective tissue disorders.
Acquired
Causes include vitamin C deficiency (scurvy), steroid therapy, normal ageing (senile purpura), amyloid in blood vessels, cryoglobulinaemia and immune complex deposition (e.g. purpura fulminans in septicaemia). Henoch–Schönlein purpura is an allergic vasculitis that follows an acute infection, usually in childhood, and may be associated with arthropathy, haematuria and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Platelets
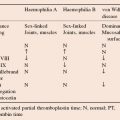
Excessive bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia or disordered platelet function is mucosal (e.g. epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding or menorrhagia) or affects the skin (purpura, petechiae and ecchymoses; Figs. 6.1, 6.2, 41.2). Symptoms usually occur when the platelet count is <10 × 109/L, but this may be higher when there is impaired platelet function. Thrombocytopenia (platelets <140 × 109/L) may be congenital or acquired (Box 41.1). Congenital forms are rare; causes include congenital aplastic anaemia, thrombocytopenia with absent radii syndrome and the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (thrombocytopenia with eczema and hypogammaglobulinaemia). Congenital infection (e.g. rubella, cytomegalovirus) frequently leads to thrombocytopenia. Acquired causes include deficient platelet production or accelerated platelet destruction.
Rare selective congenital defects of platelet production
Aplastic anaemia (Fanconi)
Part of general bone marrow failure
Cytotoxic drugs
Autoimmune
Drugs, e.g. heparin
DIC
TTP
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree