CCR4 Inhibitors
Cesar Antonio Virgen
Cecelia Alejandra Larocca
Mogamulizumab is the only FDA-approved C-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4) inhibitor. It is approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides (the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma [CTCL]) or Sézary syndrome (the leukemic form of CTCL). In Japan, mogamulizumab is also approved for the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). Mogamulizumab is a recombinant, defucosylated, humanized monoclonal antibody directed against CCR4. CCR4 is the G protein-coupled receptor for the chemokines CCL17 and CCL22, which mediate T-cell chemotaxis to the skin. CCR4 is expressed on malignant T-cells and on regulatory T-cells. Binding of mogamulizumab to CCR4 triggers antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.1
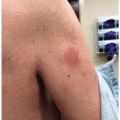
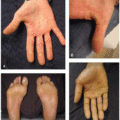
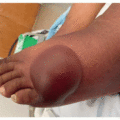
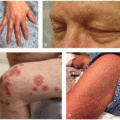
In the phase III MAVORIC clinical trial, the most common side effects were rashes, infusion-related reactions, fatigue, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, upper respiratory tract infections, and skin infections.2 Cutaneous drug eruptions were observed in 24% of patients, including 5% of patients with CTCAE grade 3 or greater. Alopecia affected 7% of patients. Conjunctivitis was seen in 5% of patients (Figure 39.1). Cutaneous adverse reactions were the leading cause for treatment discontinuation. Mogamulizumab-associated rashes (MARs) have a variety of clinical morphologies: morbilliform, lichenoid, psoriasiform or smooth papules or plaques, folliculocentric CTCL-like plaques with or without alopecia that may resemble seborrheic dermatitis, photo-accentuated dermatitis, or erythroderma (Figures 39.2,39.3,39.4).3 They are classified into three histologic reaction patterns: spongiotic/psoriasiform dermatitis, interface dermatitis, and granulomatous dermatitis, all of which can exhibit some CTCL-like features (eg, lymphocyte atypia, lymphocyte tagging, lymphocyte exocytosis, and lamellar fibroplasia).4 Photosensitivity has also been reported in patients with photo-accentuated dermatitis, in select cases resembling chronic actinic dermatitis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree