Case 2
Presentation
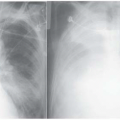
A 59-year-old man presents to your office with complaints of swelling over the right side of the neck of 3 months’ duration and otalgia for 1 month. He has been a chronic smoker for the last 30 years. Examination of the neck reveals enlarged lymph nodes at levels II and III on both sides. The largest node at the right level II measures about 4.5 × 4.5 cm and appears to be fixed to the underlying structures. Remaining nodes are less than 3 cm in diameter.
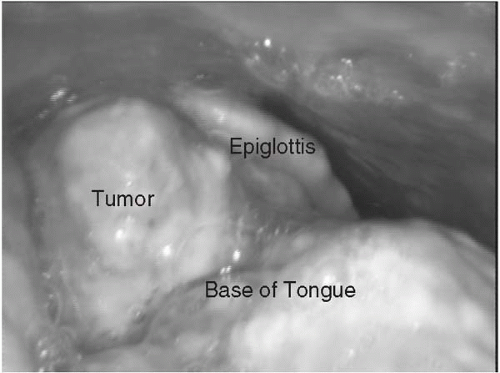
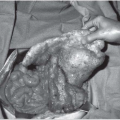
▪ Clinical Photograph
Physical Examination Report
Examination of the oral cavity reveals a proliferative growth over the base of the tongue on the right side involving the right vallecula and just reaching the midline, measuring about 4 × 4 cm. There is no extension to the larynx, and tongue movements are normal. On digital examination, induration is felt just around the lesion and reaching midline.
Differential Diagnosis
A provisional diagnosis is made of malignant tumor of the base of the tongue with secondary metastasis to the neck lymph nodes. The patient is advised to undergo biopsy from the base of the tongue and fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of the right cervical lymph node. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the neck and radiography of the chest is also advised.
Discussion
Squamous cell carcinoma of the base of the tongue usually presents as neck swelling, though some patients present with complaints of change in voice, foreign body sensation in throat, referred otalgia, odynophagia, and dysphagia. With involvement of the larynx, the patients can develop stridor. The differential diagnosis for the exophytic lesions over the base of the tongue includes benign lesions like lymphoid hyperplasia, lingual thyroid, papillomas, benign tumors of the minor salivary glands, peripheral giant cell granulomas, and migratory glossitis. Most common malignant tumors of the base of the tongue are squamous cell carcinomas, which account for about 70% of cases. About 20% are lymphomas, and the remainder are minor salivary gland tumors. Other less common malignant tumors are sarcomas, adenocarcinomas from the lingual thyroid, and metastatic tumors.
Case Continued
The patient undergoes a punch biopsy from the base of the tongue lesion and FNAC from the right level II node. The biopsy is reported as squamous cell carcinoma with moderate differentiation. The FNAC is reported as metastatic deposits of squamous cell carcinoma.
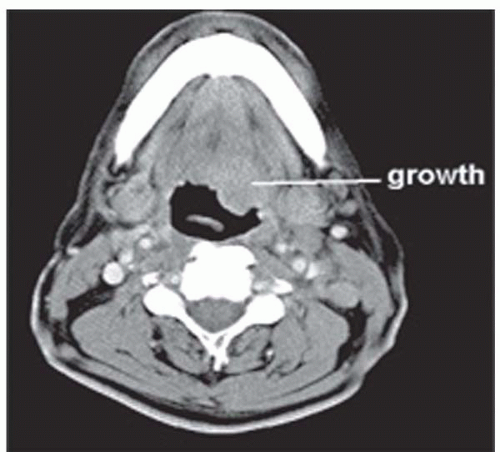
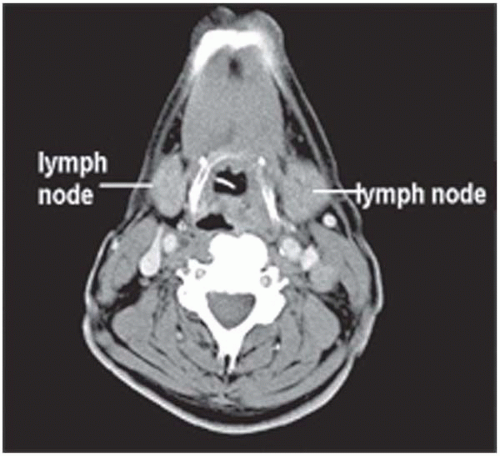
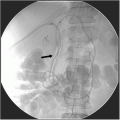
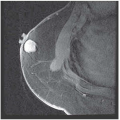
▪ CT Scans
CT Scan Report
The CT scan shows an infiltrative lesion at the base of the tongue on the right side involving the vallecula. The extrinsic muscles of the tongue, pterygoid muscles, and larynx are free of disease. Level II and III nodes are present bilaterally. The largest node is about 4 cm in diameter and is present at right level II. Chest radiography is unremarkable.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree