Campylobacteriosis
Contact Precautions
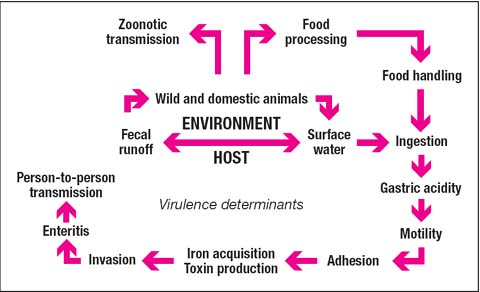
Campylobacteriosis is an intestinal infection caused by Campylobacter, which are spiral-shaped bacteria that invade and destroy the epithelial cells of the jejunum, ileum, and colon. The bacteria may spread to the bloodstream in people with compromised immune systems, causing a life-threatening infection. Most people recover in 2 to 5 days, although recovery may take up to 10 days in some.
Causes
Campylobacteriosis is transmitted via consumption of contaminated food, such as raw poultry, fresh produce, water, or unpasteurized milk, and through contact with the stool of an infected person. Transmission can also result from contact with the stool of infected pets and wild animals. Risk factors include recent family history of infection with C. jejuni and travel to an area with poor hygiene or sanitation practices.
Campylobacteriosis is transmitted by ingesting contaminated food, such as raw poultry, fresh produce, water, or unpasteurized milk, and through contact with infected stool. Only a few organisms are needed to cause illness in humans. One drop of liquid from raw chicken meat can cause infection in a person. An estimated 100 people die from C. jejuni infections each year in the United States.
 |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


