Bullous Reactions
Rohit Gupta
Anisha B. Patel
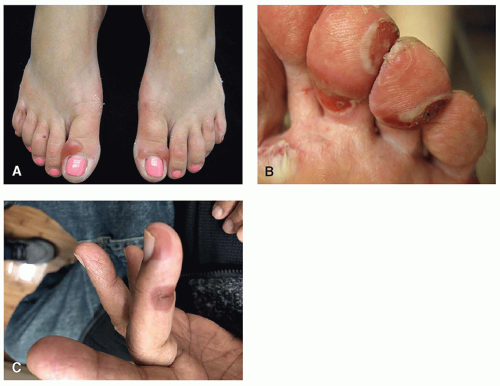
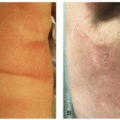
Bullous reactions represent a group of skin toxicities characterized by fluid-filled vesicles or bullae with varying localized or diffuse presentations depending on the drug class. Many reaction patterns have bullous variants. Specifically, morbilliform reactions may progress to more significant eruptions, including Steven’s-Johnson syndrome (SJS). Both hand-foot syndrome (HFS) and hand-foot skin reaction (HFSR) may present with bullae on the feet in the setting of more severe disease (Figure 8.1). Intertriginous eruptions may have vesicles or bullae that precede erosions in the folds of the skin. With toxicities associated
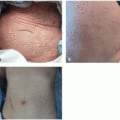
with edema, bullae may be present and are generally edematous and isolated to the edematous areas of involvement. Various presentations of skin disease in the setting of checkpoint blockade can present with bullae, including bullous lichenoid eruptions (Figure 8.2), vesicular Grover’s disease, and autoimmune bullous disease, the focus of the remainder of this chapter.
with edema, bullae may be present and are generally edematous and isolated to the edematous areas of involvement. Various presentations of skin disease in the setting of checkpoint blockade can present with bullae, including bullous lichenoid eruptions (Figure 8.2), vesicular Grover’s disease, and autoimmune bullous disease, the focus of the remainder of this chapter.
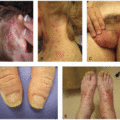
The most common immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-induced bullous eruption is bullous pemphigoid (BP), which represents a rare but serious cutaneous adverse event that occurs in approximately 1% of patients treated with immunotherapy targeting PD-1 or PD-L1; it has been less commonly associated with anti-CTLA-4 therapy.1,2 Generally, patients present with tense bullae affecting the limbs or trunk on a
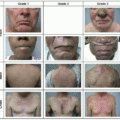
background of normal or mildly erythematous skin (Figure 8.3). In terms of timing, the onset of bullous reactions typically occur may as early as 3 weeks after drug initiation, though presentations are typically more delayed with onset after 6 months not uncommon.3 Patients may experience a prodrome of a pruritic, urticarial-appearing rash weeks before the development of bullae. Importantly, some patients may present only with urticarial or eczematous papules and plaques and thus the spectrum and extent of disease can be quite varied (Figure 8.4); this makes the diagnosis of immunotherapy-induced BP potentially challenging. However, accurate diagnosis is critical for initiating disease-specific interventions.
background of normal or mildly erythematous skin (Figure 8.3). In terms of timing, the onset of bullous reactions typically occur may as early as 3 weeks after drug initiation, though presentations are typically more delayed with onset after 6 months not uncommon.3 Patients may experience a prodrome of a pruritic, urticarial-appearing rash weeks before the development of bullae. Importantly, some patients may present only with urticarial or eczematous papules and plaques and thus the spectrum and extent of disease can be quite varied (Figure 8.4); this makes the diagnosis of immunotherapy-induced BP potentially challenging. However, accurate diagnosis is critical for initiating disease-specific interventions.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree