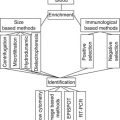
Gene
Description
Function(s)
Signature type and importance
Annexin A5 (ANXA5)
Gene encodes indirect inhibitor of the thromboplastin-specific complex involved in the blood coagulation cascade
Calcium ion binding, calcium-dependent phospholipid binding, phospholipase inhibitor activity, phospholipid binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Actin, gamma 1 (ACTG1)
Gene encodes a cytoplasmic actin found in nonmuscle cells
ATP binding, identical protein binding, protein binding, structural constituent of cytoskeleton
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
ADP ribosylation factor 3 (ARF3)
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ARF-like (ADP ribosylation factor-like) subfamily of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins which are involved in regulation of intracellular traffic
GTP binding, metal ion binding, phospholipid binding, protein binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
ATPase, Na+/K + transporting, beta 3 polypeptide (ATP1B3)
Family of gene product is Na+/K+−ATPase which is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane
Sodium/potassium-exchanging ATPase activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
HLA-B associated transcript 3 (BAT3)
Gene encodes a nuclear protein that is cleaved by caspase 3 and is implicated in the control of apoptosis
Hsp70 protein binding, polyubiquitin binding, proteasome binding, protein binding, ribosome binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Other name: BAG6 (BCL2-associated athanogene 6)
Caldesmon 1 (CALD1)
Gene encodes a calmodulin- and actin-binding protein that plays an essential role in the regulation of smooth muscle and nonmuscle contraction
Actin binding, calmodulin binding, myosin binding, tropomyosin binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Centaurin, delta 2 (CENTD2)
Gene encodes a protein that associates with the Golgi, and the ARF-GAP activity mediates changes in the Golgi and the formation of filopodia
Zinc ion binding, protein binding, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding, Rho GTPase activator activity, ARF GTPase activator activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Other name: ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 1 (ARAP1)
Chloride intracellular channel 1 (CLIC1)
Chloride intracellular channel 1 is a member of the p64 family; the protein localizes principally to the cell nucleus and exhibits both nuclear and plasma membrane chloride ion-channel activity
Chloride channel activity, protein binding, voltage-gated chloride channel
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Chitobiase di-N-acetyl (CTBS)
Chitobiase is a lysosomal glycosidase involved in degradation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on glycoproteins
Chitinase activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 (DPYSL3)
DHPases are a family of enzymes that catalyze the reversible hydrolytic ring opening of the amide bond in five- or six-membered cyclic diamides
SH3 domain binding, chondroitin sulfate binding, hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in cyclic amides, phosphoprotein binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Dishevelled, dsh homolog 3 (DVL3)
Gene encodes a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that regulates cell proliferation
Beta-catenin binding, protease binding, receptor binding, signal transducer activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Exostoses 1 (EXT1)
Gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum-resident type II transmembrane glycosyltransferase involved in the chain elongation step of heparan sulfate biosynthesis
Heparan sulfate N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity, protein heterodimerization activity, protein homodimerization activity, transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1)
Protein encoded by this gene binds both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and is involved in limb induction
Heparin binding, protein tyrosine kinase activity, ATP binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Ferritin, light polypeptide (FTL)
Gene encodes the light subunit of the ferritin protein which is the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Ferric iron binding, iron ion binding, oxidoreductase activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Guanine nucleotide binding protein: GNB2L1
WD40 domain encoded by gene is found in a number of eukaryotic proteins that cover a wide variety of functions including adaptor/regulatory modules in signal transduction
Protein complex scaffold, protein kinase C, protein tyrosine kinase activity, receptor binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (HIF1A)
HIF-1 functions as a master regulator of cellular and systemic homeostatic response to hypoxia
Signal transducer activity, DNA binding transcription factor activity, protein kinase binding, histone deacetylase binding, enzyme binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 1 (IL13RA1)
Gene encodes a subunit of the interleukin 13 receptor. This subunit forms a receptor complex with IL4 receptor alpha, a subunit shared by IL13 and IL4 receptors
Cytokine receptor activity, protein binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Lipin 2 (LPIN2)
According to mouse experiments, gene functions during normal adipose tissue development and may play a role in human triglyceride metabolism
Phosphatidate phosphatase activity, transcription coactivator activity
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Staufen, RNA binding protein (STAU1)
Staufen is a member of the family of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding proteins involved in the transport and/or localization of mRNAs to different subcellular compartments and/or organelles
Double-stranded RNA binding, protein binding
Signature A 1 implying shorter distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Activity-dependent neuroprotector (ADNP)
This gene encodes a protein that is upregulated by vasoactive intestinal peptide and may be involved in its stimulatory effect on certain tumor cells
Chromatin binding, metal ion binding, sequence specific DNA binding, protein binding
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
ATPase, H + transporting, lysosomal accessory protein 1 (ATP6AP1)
This gene encodes a component of a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles
ATP binding proton-transporting ATP synthase activity-rotational mechanism, proton-transporting ATPase activity-rotational mechanism, transporter activity
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Basic leucine zipper transcription factor, ATF-like (BATF)
Gene encodes nuclear basic leucine zipper protein that belongs to the AP-1/ATF superfamily of transcription factors
Protein binding, sequence specific DNA binding
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Clathrin, heavy polypeptide (CLTC)
Clathrin is a major protein component of the cytoplasmic face of intracellular organelles
Protein binding, structural molecule activity
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Coiled-coil and C2 domain containing 1A (CC2D1A)
This gene encodes a transcriptional repressor that binds to a conserved 14-bp 5′-repressor element and regulates expression of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1A gene in neuronal cells
Signal transducer activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence specific DNA binding
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1)
IRF1 serves as an activator of interferons alpha and beta transcription
Sequence specific DNA binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence specific DNA binding
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Plexin A3 (PLXNA3)
This gene encodes a class 3 semaphorin receptor and may be involved in cytoskeletal remodeling and apoptosis
Semaphoring receptor activity, transmembrane signaling receptor activity
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Sorting nexin 5 (SNX5)
This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family
Phosphatidylinositol binding
Signature B 1 implying longer distant metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients
Invasiveness Gene Signature
Liu’s group has formed another gene signature called as “invasiveness gene signature (IGS)” (Table 12.2) including differentially expressed 186 genes in CD44+CD24−/low breast cancer stem cells compared to normal breast epithelial cells [34]. IGS is used for association between gene expression levels and patient survival and risk of death. This association is made upon some bioinformatic analysis. Pearson correlation coefficients positive (>0) and negative (≤0) are found for patients in data set. These two coefficients imply two patient groups: one is positively related with IGS, which corresponds to positive correlation coefficient, and the other group of patients has negative correlation coefficient and negatively related with IGS. Positive correlation coefficient means higher risk of metastasis and reduced overall survival, and negative correlation coefficient has the opposite meaning for patients. Analysis of 295 breast cancer patients revealed that 62 % of patients, whose gene expression levels show similarity with IGS (correlation coefficient, >0), could survive in estimated 10 years of overall survival. The metastasis-free survival ratio is 54 % for those patients with positive correlation coefficient. The survival picture is better for patients whose gene profiling is negatively related to IGS (correlation coefficient, ≤0). Overall survival ratio of these patients is 98 % and metastasis-free survival is 82 % in estimated 10 years. From these results, it is possible to conclude that invasiveness gene signature has prognostic significance for breast cancer patients.
Table 12.2
Some genes included in invasiveness gene signature (IGS)
Gene | Description | Function(s) | Gene functional subgroup in all other IGS genes |
|---|---|---|---|
Zinc and double PHD fingers family 2 (DPF2) | The protein encoded by this gene functions as a transcription factor which is necessary for the apoptotic response following deprivation of survival factors | Zinc ion binding, apoptotic process | Apoptosisa |
B cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL2) | This gene encodes an integral outer mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks the apoptotic death of some cells such as lymphocytes | B cell and T cell homeostasis, apoptosis, axon regeneration, cell aging, developmental growth, cell-cell adhesion | Apoptosisa |
Secretagogin, EF-hand calcium-binding protein (SCGN) | The encoded protein is a secreted calcium-binding protein which is found in the cytoplasm | Calcium ion binding | Calcium ion bindinga |
alkB, alkylation repair homolog 1 (ALKBH1) | This gene encodes a homolog to the E. coli alkB gene product, which is part of the adaptive response mechanism of DNA alkylation damage repair | DNA demethylation, DNA repair, neuron migration, developmental growth, ferrous iron binding | Cell cyclea |
CD59 molecule, complement regulatory protein (CD59) | This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that regulates complement-mediated cell lysis, and it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction | Cell activation, blood coagulation, innate immune response, complement binding | Cell surface receptora |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 (MAPK14) | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family, which acts as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and is involved in a wide variety of cellular processes | Angiogenesis, blood coagulation, cell morphogenesis, chemotaxis, MAP kinase activity | Chemotaxisa |
Matrix metallopeptidase 7 (MMP7) | The enzyme encoded by this gene degrades proteoglycans, fibronectin, and elastin | Proteolysis, antibacterial peptide secretion, regulation of cell proliferation | Collagen metabolisma |
Matrix Gla protein (MGP) | The protein encoded by this gene is secreted and likely acts as an inhibitor of bone formation | Cell differentiation, calcium ion binding, cartilage condensation | Differentiationa |
Sodium channel modifier 1 (SCNM1) | SCNM1 is a zinc finger protein and putative splicing factor | Metal ion binding, RNA splicing | Ion-channel activitya |
Toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 2 (TICAM 2) | TICAM 2 is a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor | Inflammatory response, innate immune response, toll-like receptor signaling pathway, signal transducer activity | Membrane proteina |
Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (GNPDA1) | Gene encodes an allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of d-glucosamine-6-phosphate into d-fructose-6-phosphate and ammonium | Hydrolase activity, single fertilization, glucosamine catabolic process | Metabolisma |
DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha (DNMT3A) | This gene encodes a DNA methyltransferase that is thought to function in de novo methylation, rather than maintenance methylation | DNA methylation, spermatogenesis, cellular response to amino acid stimulus | Methyltransferasea |
Actin-related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 5 (ARPC5) | This gene encodes one of seven subunits of the human Arp2/3 protein complex, which controls of actin polymerization in cells | Actin binding, innate immune response, actin cytoskeleton organization | Morphologya |
Nucleolar protein 8 (NOL8) | NOL8 binds Ras-related GTP-binding proteins | RNA binding, DNA replication, positive regulation of cell growth | Nucleotide bindinga |
Dual specificity phosphatase 10 (DUSP10) | Gene product inactivates their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues | Protein dephosphorylation, response to stress, inactivation of MAPK activity, negative regulation of JNK cascade | Phosphatasea |
v-erb-b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4 (ERBB4) | Gene encodes a member of the Tyr protein kinase family and the epidermal growth factor receptor subfamily | Cell migration, cell proliferation, lactation, innate immune response, heart development | Proliferationa |
Cleavage stimulation factor, 3′ pre-RNA, subunit 1 (CSTF1) | This gene encodes one of three subunits, which combine to form cleavage stimulation factor (CSTF). CSTF is involved in the polyadenylation and 3′ end cleavage of pre-mRNAs | RNA binding, splicing, mRNA polyadenylation, gene expression | Protein bindinga |
p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) | The p21-activated kinases (PAK) are critical effectors that link Rho GTPases to cytoskeleton reorganization and nuclear signaling | Apoptotic process, axon guidance, innate immune response, phosphorylation, viral process, ATP binding, protein kinase activity, T cell costimulation | Protein kinasea |
Nucleoporin 37 kDa (NUP37) | Nuclear pore complexes are composed of subcomplexes, and NUP37 is part of one such subcomplex | Mitosis, cell division, glucose transport, protein transport, transmembrane transport | Protein transporta |
Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) | The encoded protein may play a role in the regulation of renal and intestinal calcium and phosphate transport, cell metabolism, or cellular calcium/phosphate homeostasis | Hormone activity, response to cellular stress, cell-cell signaling, embryo implantation | Signal transductiona |
Ataxin 3 (ATXN3) | The protein encoded by this gene contains (CAG)n repeats in the coding region, and the expansion of these repeats from the normal 13–36 to 68–79 is one cause of Machado-Joseph disease | Cell death, cellular response to heat, nucleotide excision repair | Transcription factora |
Heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase 1 (HS2ST1) | This gene encodes a member of the heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzyme family that transfers sulfate to the 2 position of the iduronic acid residue of heparan sulfate | Sulfotransferase activity, carbohydrate metabolic process | Transferasea |
Membrane-associated ring finger (C3HC4) 8, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (MARCH8) | MARCH8 is a member of the MARCH family of membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases | Zinc ion binding, protein polyubiquitination, MHC class II protein binding | Ubiquitinationa |
Human Normal Mammary Stem Cell (hNMSC) Signature
hNMSC signature includes 1,090 upregulated genes and 1,217 downregulated genes in PKH26+ cells. (Since the gene signature involves a long list of genes, it will not be presented here as a table.) Then, gene profiles of different graded breast tumors (G3, less differentiated; G1, highly differentiated) are examined via gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and compared with hNMSC signature. G3 tumors’ gene profiling demonstrates high hNMSC signature identity, but G1 tumors’ gene profile is not so similar. This implies that G3 tumors have more breast cancer stem cells. In other words, they are less differentiated, which is a previously known feature of tumor. Therefore, hNMSC signature has been found as a useful tool to predict breast tumor grade [20].
hNMSC signature is different from other breast cancer stem cell-related gene signatures because it is formed from healthy individual normal mammary stem cells. However, it is possible to use it for prediction of breast tumor grades. Also, hNMSC signature and breast tumor grade-3 correlation (but noncorrelation between this signature and G1 tumors) show that different breast tumor grades have different breast cancer stem cell contents. Therefore, in the future, hNMSC signature may play important roles in breast cancer therapy.
The 31-Gene Signature of Breast Cancer Stem Cell Subgroups
Microarray analysis of two distinct subsets of breast cancer stem cells (CD44+/CD24− and CD44+/CD24− cells) revealed 1,777 upregulated genes and 1,883 downregulated genes [35]. CD44+/CD24− cells showed more than twofold significance for 599 of these genes compared to the CD44+/CD24− group. Higher cancer stem cell capacity of CD44+/CD24− cells is found compared to the other group. A total of 198 untreated breast cancer patients are examined; 64 ER (negative) group patients are used as a training set. The aim of forming a training set is that some of 599 genes can be used in the prediction of patients’ distant metastasis situations. Twenty-five of 64 patients demonstrated distant metastasis and K-nearest neighbor algorithm as classifier is used to identify a 31-gene signature (Table 12.3). Also, this signature has been validated in another test group. Sensitivity of the signature is 70 % and specificity is 97 %. Patients who will not experience distant metastasis can be predicted more accurately because of high specificity.
Table 12.3
Some important genes from 31-gene signature
Gene | Description | Function(s) |
|---|---|---|
Suppression of tumorigenicity 14 (ST14) | The protein encoded by this gene is an epithelial-derived, integral membrane serine protease | Serine-type peptidase activity, proteolysis |
Annexin A6 (ANXA6) | Annexin VI belongs to a family of calcium-dependent membrane and phospholipid binding proteins
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|