Fresh frozen plasma
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is a source of all coagulation and other plasma proteins. Compatibility testing is not required, but blood group compatible units are used. FFP from group AB donors may be used if the recipient blood group is unknown. As FFP is not heat sterilized and may transmit infection, solvent-treated FFP is safer in this regard.
Indications
- Coagulation factor replacement. Perform coagulation tests and platelet count prior to use. Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) or massive transfusion at risk of bleeding and with coagulation abnormalities may benefit. Single-factor deficiencies are best treated with a specific factor concentrate.
- Liver disease – in the presence of bleeding or prior to invasive procedures, e.g. liver biopsy; combined with vitamin K.
- Haemolytic uraemic syndrome or thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura usually with plasma exchange. Cryoprecipitate-poor FFP is preferred.
- Reversal of warfarin or direct factor Xa or factor II inhibitor anticoagulation or thrombolytic therapy.
Cryoprecipitate
Cryoprecipitate is prepared from the precipitate formed from FFP during controlled thawing, resuspended in 20-mL plasma. It is rich in fibrinogen, fibronectin and factor VIII. Group compatible units are used. It may be useful in patients with DIC, liver disease, following massive transfusion and, rarely, in von Willebrand disease.
Other blood products
These are derived from pooled human plasma that has undergone a manufacturing process designed to concentrate and sterilize the component. They carry a theoretical risk of transmitting diseases caused by prions (e.g. nvCJD). There have been no fully documented cases of this with blood products other than red cell transfusions, but the current UK practice is to use products made by recombinant DNA or plasma from non-UK donors.
Coagulation factor concentrates
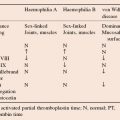
Coagulation factor concentrates are available as freeze-dried powder of high purity. Factor VIII concentrate is used for treatment of haemophilia A and von Willebrand disease; recombinant factor VIII is now available. Factor IX concentrate, also available as recombinant, is used in patients with haemophilia B. Factor IX complex (prothrombin complex) also contains factors II, VII and X and is of value in patients with specific disorders involving factors II and X, oral anticoagulant overdose, in severe liver failure and to overcome inhibitors to factor VIII in patients with haemophilia A who have developed inhibitors. Its use carries a risk of provoking thrombosis and DIC.
Other concentrates include protein C, antithrombin, factors VII, XI and XIII. They are used in the corresponding congenital deficiencies. Protein C concentrate is also used in severe DIC, e.g. meningococcal septicaemia.
Recombinant human factor VIIa
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree