The classification applies to carcinomas. Papilloma is excluded. There should be histological or cytological confirmation of the disease. The regional lymph nodes are the nodes of the true pelvis, which essentially are the pelvic nodes below the bifurcation and those along the common iliac arteries. Laterality does not affect the N classification. The suffix (m) should be added to the appropriate T category to indicate multiple tumours. The suffix (is) may be added to any T to indicate presence of associated carcinoma in situ. The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
URINARY BLADDER (ICD‐O‐3 C67)
Rules for Classification
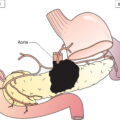
Anatomical Subsites (Fig. 524)
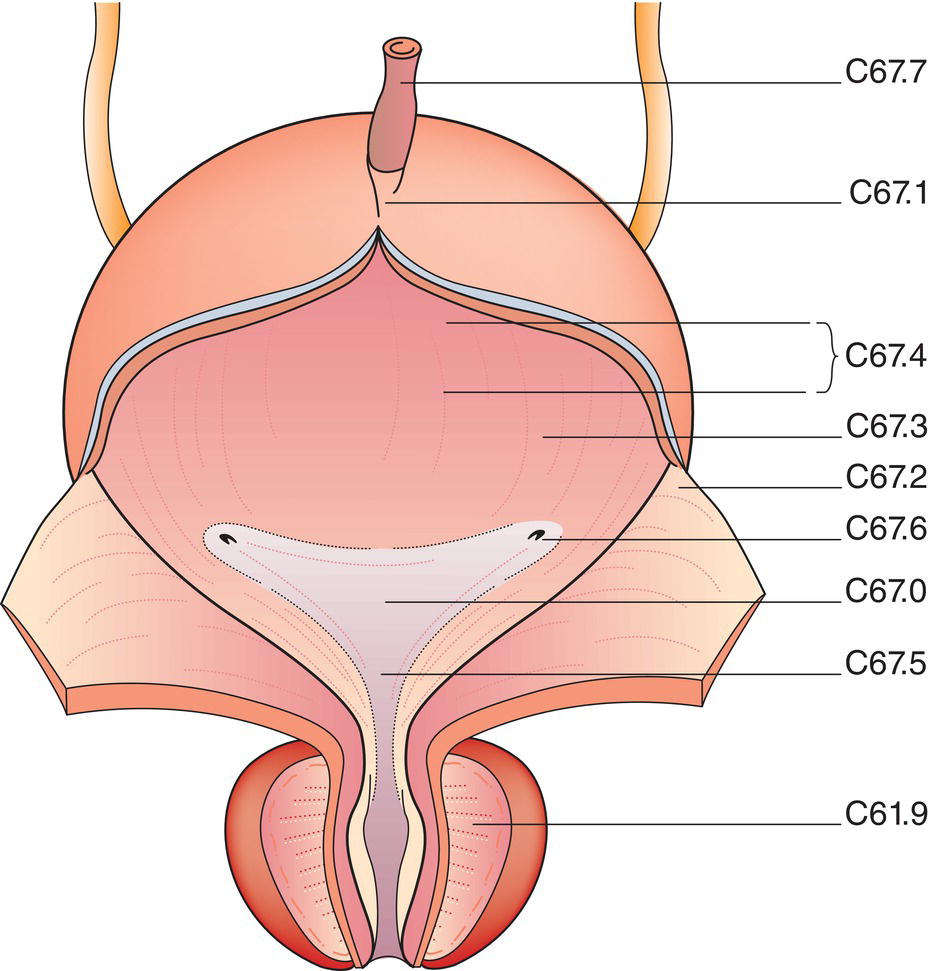
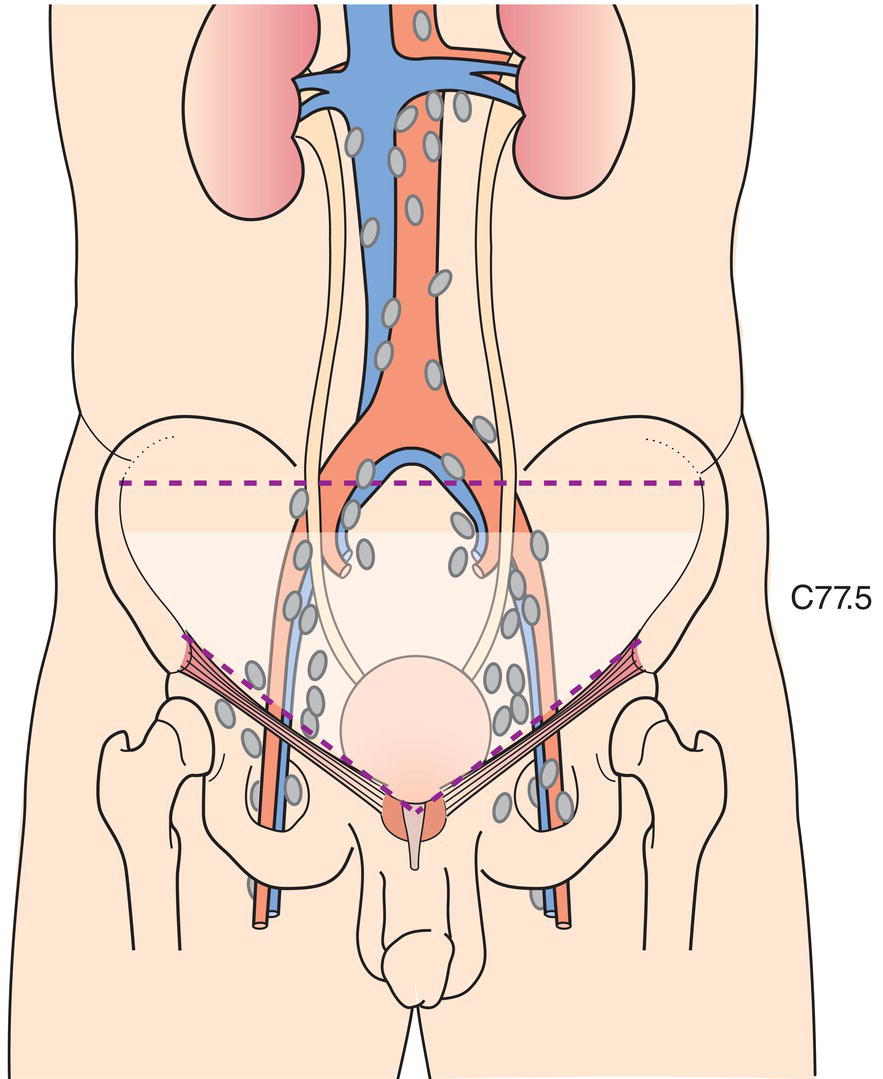
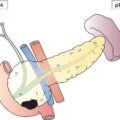
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 525)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour (Fig. 526)
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Ta
Noninvasive papillary carcinoma
Tis
Carcinoma in situ: “flat tumour”
T1
Tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue
T2
Tumour invades muscularis propria
T2aTumour invades muscularis propria (inner half)
T2b Tumour invades deep muscularis propria (outer half)
T3
Tumour invades perivesical tissue:
T3a microscopically
T3b macroscopically (extravesical mass)
T4
Tumour invades any of the following: prostate stroma, seminal vesicles, uterus, vagina, pelvic wall, abdominal wall
T4a Tumour invades prostate stroma, seminal vesicles, uterus, or vagina
T4b Tumour invades pelvic wall or abdominal wall 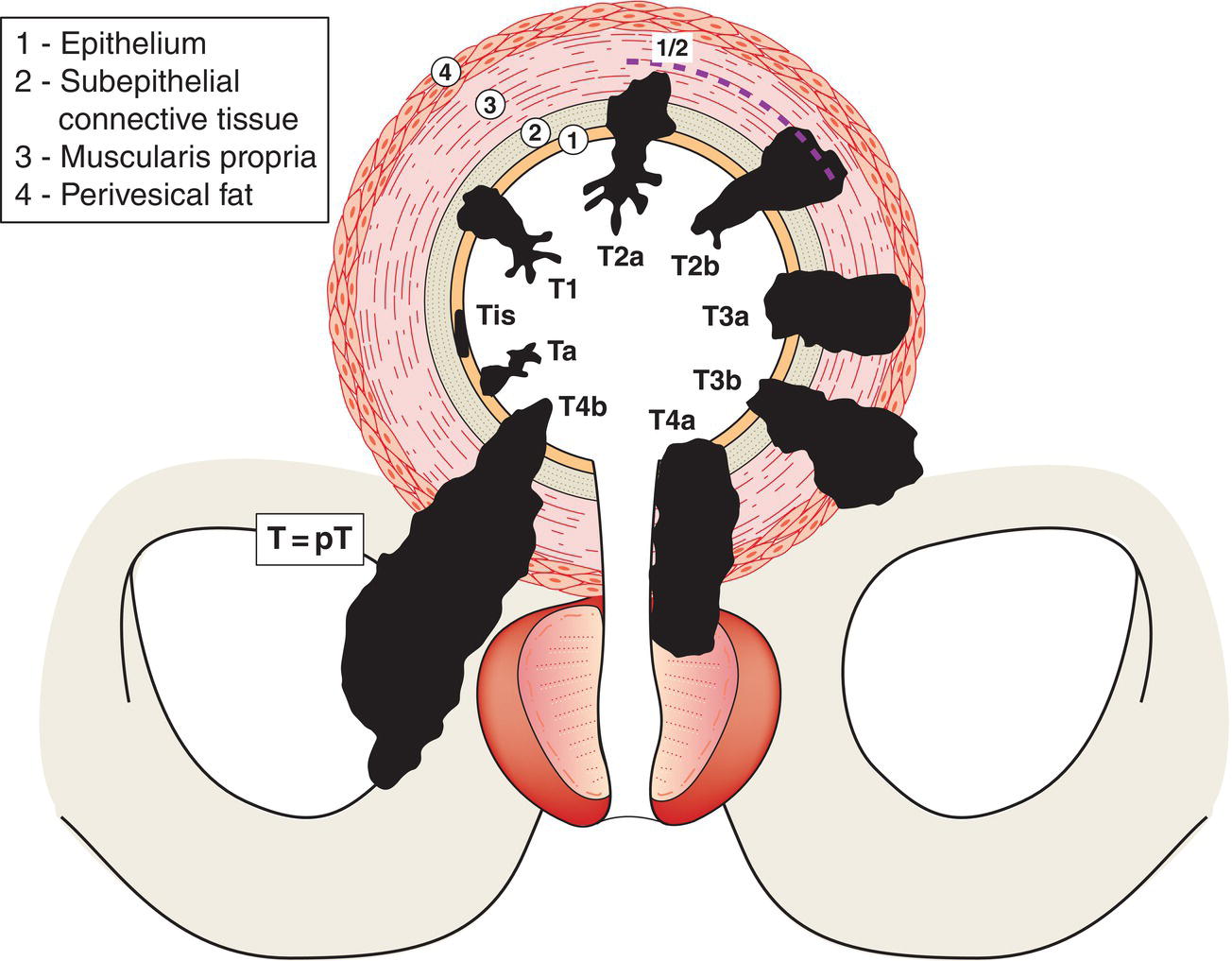
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
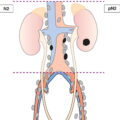
N1
Metastasis in a single lymph node in the true pelvis (hypogastric, obturator, external iliac, or presacral) (Fig. 527)
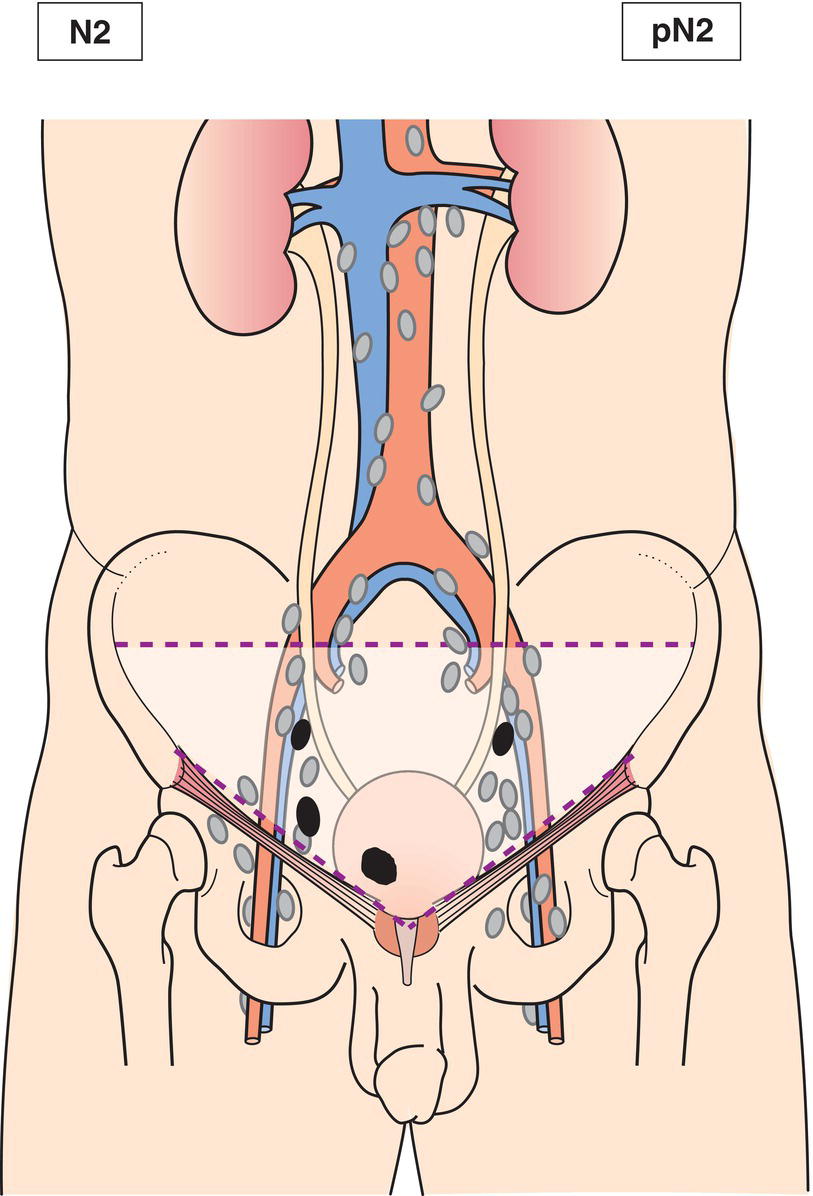
N2
Metastasis in multiple regional lymph nodes in the true pelvis (hypogastric, obturator, external iliac, or presacral) (Fig. 528)
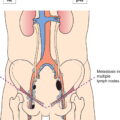
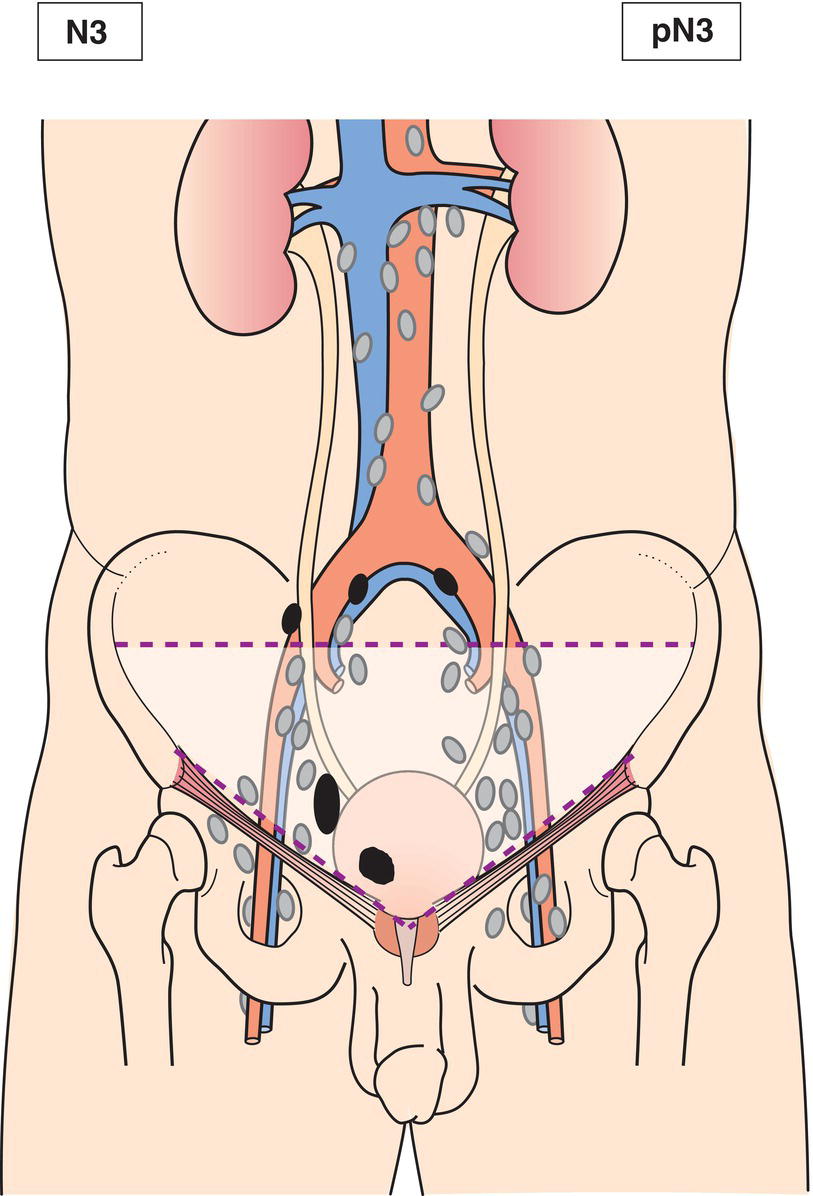
N3
Metastasis in a common iliac lymph node(s) (Fig. 529) 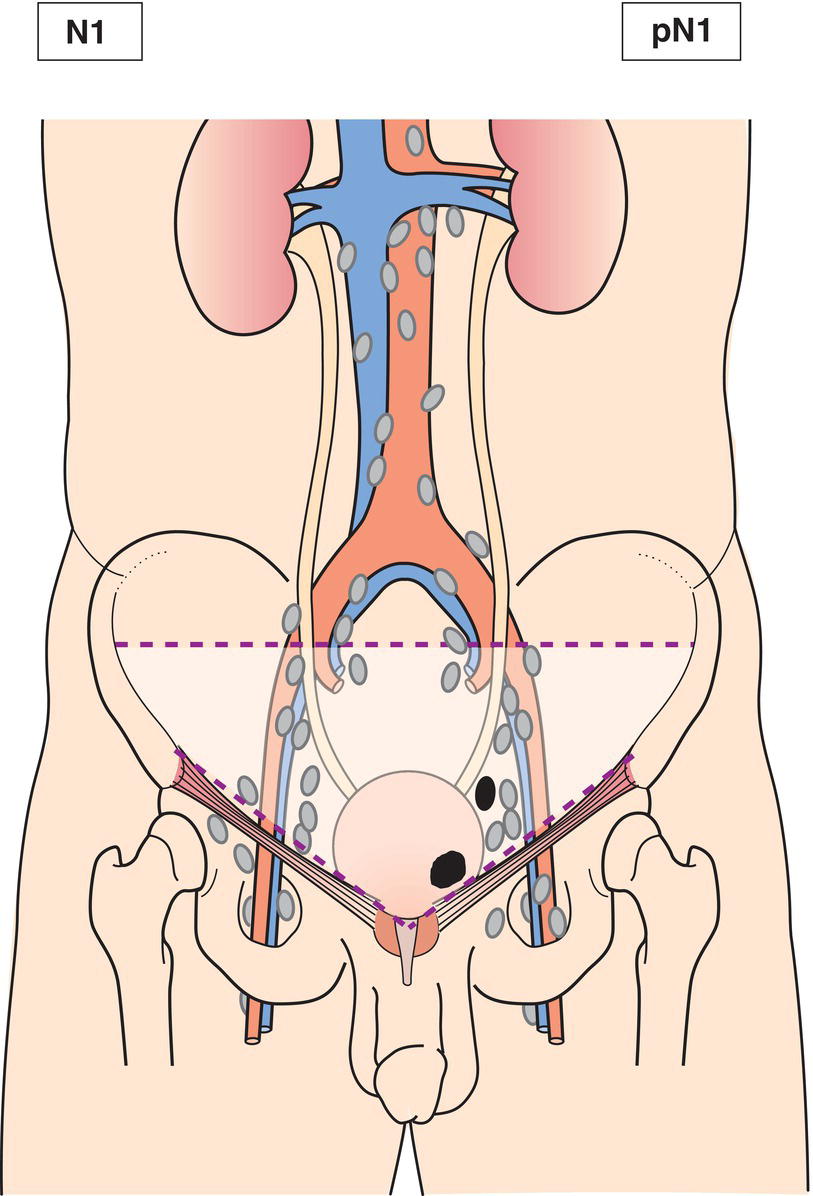
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1aM1b
Non‐regional lymph nodesOther distant metastasis
pTNM Pathological Classification
pM1a pM1b
Non‐regional lymph nodesOther distant metastasis
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree