Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is an opportunistic infection caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus, usually A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger. Aspergillosis occurs in four major forms: aspergilloma, which produces a fungus ball in the lungs (called a mycetoma); allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, a hypersensitive asthmatic reaction to Aspergillus antigens; aspergillosis endophthalmitis, an infection of the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye that can lead to blindness; and invasive aspergillosis, an acute infection that produces septicemia, thrombosis, and infarction of virtually any organ, but especially the heart, lungs, brain, and kidneys.
Aspergillus may cause infection of the ear (otomycosis), cornea (mycotic keratitis), and prosthetic heart valves (endocarditis); pneumonia (especially in patients receiving immunosuppressants, such as antineoplastic agents or high-dose steroids); sinusitis; and brain abscesses.
The prognosis varies with each form. Occasionally, aspergilloma causes fatal hemoptysis.
Causes
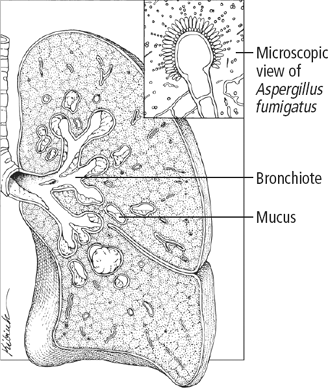
Aspergillus is found worldwide, commonly in decaying vegetation, such as dead leaves, stored grain, compost piles, and damp hay. It can also be found in household dust, building materials, and some food items. Transmission is by inhalation of fungal spores or, in aspergillosis endophthalmitis, by the invasion of spores through a wound or other tissue injury. It’s a common laboratory contaminant. (See Aspergillus infection.)
Aspergillus produces clinical infection only in people who become especially vulnerable to it. Such vulnerability can result from excessive or prolonged use of antibiotics, glucocorticoids, or other immunosuppressive agents; from radiation; from such conditions as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, Hodgkin’s disease, leukemia, azotemia, alcoholism, sarcoidosis, bronchitis, or bronchiectasis; from organ transplants; and, in aspergilloma, from tuberculosis or another cavitary lung disease.
After the Aspergillus spores are inhaled, they cause mucus buildup in the lungs, which in turn leads to wheezing, dyspnea, cough with some sputum production, hemoptysis, pleural pain, and fever.
 |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


