Chapter 16
A Primer on Vaccines
At the conclusion of the chapter, the reader should be able to:
• Identify the federal agency that regulates vaccine products.
• Describe vaccine policy and the role of vaccines in public safety.
• Briefly describe the history and use of several specific vaccines.
• Explain some new targets and technologies for vaccines.
• Identify at least three essential characteristics of a vaccine.
• Based on immunologic principles, describe the host response to vaccination.
• Analyze the problems associated with AIDS vaccine development and use.
• Describe the development and application of human papillomavirus vaccine.
• Compare and contrast the applications of at least four vaccines.
• Correctly answer case study related multiple choice questions.
• Be prepared to participate in a discussion of critical thinking questions.
• Describe the principle and clinical application of the tetanus antibodies assay.
Applications of Vaccines
• A boom in scientific discovery and the production of vaccines
• A desire to protect children from significant outbreaks of infectious diseases, including polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and pertussis (whooping cough)
• An increase in the birth rate among more educated and affluent parents, who accepted the use of vaccines
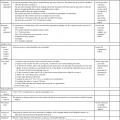
Despite public fears, American children now receive vaccinations to numerous diseases that were once common childhood infectious diseases. In the United States, the recommended childhood immunization schedule now includes vaccines to protect against 15 diseases, including seasonal influenza. Immunization schedules vary by age and by country (Tables 16-1 to 16-3, A and B).
Table 16-1
Childhood Vaccination Schedule, South Africa, 2011
| Age | Vaccine (No. of Doses) |
| At birth | BCG, vaccine against tuberculosis; trivalent oral polio vaccine (TOPV) |
| 6 wk | TOPV (one); rotavirus vaccine (RV) oral (one); DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine (one); hepatitis B vaccine (one); PCV7 pneumococcal vaccine (one) |
| 10 wk | DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine (two); DTaP (two); hepatitis B vaccine (two) |
| 14 wk | RV, oral rotavirus vaccine (two); DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine (three); hepatitis B vaccine (three); PCV7, pneumococcal vaccine (two) |
| 9 mo | Measles vaccine (one); PCV7, pneumococcal vaccine (three) |
| 18 mo | DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine (four); measles vaccine (two) |
| 6 yr | Td vaccine |
| 12 yr | Td vaccine |
From South African Vaccination and Immunisation Centre: www.savic.ac.za.
Table 16-2
Recommended Immunizations for Children, Birth Through 6 Years Old, United States, 2011
| Age | Vaccine |
| Birth | Hepatitis B (HepB) 11 |
| 1 mo | HepB 22 |
| 2 mo | HepB 2, if not given at 1 mo; rotavirus vaccine (RV)2; diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP)3; Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib)4; pneumococcal vaccine (PCV)5; inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV)6 |
| 4 mo | RV2; DTaP3; Hib4; PCV5; IPV6 |
| 6 mo | HepB 3 (6-18 mo)1; RV2; DTaP3; Hib4; PCV5; IPV (6-18 mo)6; influenza yearly7 (6 mo-6 yr) |
| 12 mo | Hib4; PCV5; measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) (12-15 mo)8; varicella (12-15 mo)9; hepatitis A (HepA)10 (12-23 mo); second dose should be given 6-18 mo later |
| 15 mo | DTaP3 |
| 18 mo | Influenza yearly7 |
| 2-3 yr | Influenza yearly7 |
| 4-6 yr | Influenza yearly7; DTaP3; IPV6; MMR8; varicella9 |
Note: Meningococcal conjugate vaccine, quadrivalent (MCV4), minimum age, 2 yr.
• Administer two doses of MCV4 at least 8 wk apart, children aged 2-10 yr with persistent complement component deficiency and anatomic or functional asplenia, and one dose every 5 yr thereafter.
• Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection who are vaccinated with MCV4 should receive two doses at least 8 wk apart.
• Administer one dose of MCV4 to children aged 2-10 yr who travel to countries with highly endemic or epidemic disease and during outbreaks caused by a vaccine serogroup.
• Administer MCV4 to children at continued risk for meningococcal disease who were previously vaccinated with MCV4 or meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine after 3 yr if first dose was administered at age 2-6 yr.
1Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB) (minimum age, birth).
•Administer monovalent HepB to all newborns before hospital discharge.
•If mother is hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive, administer HepB and 0.5 mL of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) within 12 hr of birth.
•If mother’s HBsAg status is unknown, administer HepB within 12 hours of birth. Determine mother’s HBsAg status as soon as possible and, if HBsAg-positive, administer HBIG (no later than age 1 wk).
Doses following the birth dose:
•The second dose should be administered at age 1 or 2 mo. Monovalent HepB should be used for doses administered before age 6 wk .
•Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should be tested for HBsAg and antibody to HBsAg 1-2 mo after completion of at least three doses of the HepB series, at age 9-18 mo (generally at the next well-child visit).
•Administration of four doses of HepB-infants is permissible when a combination vaccine containing HepB is administered after the birth dose.
•Infants who did not receive a birth dose should receive three doses of HepB on a schedule of 0, 1, and 6 mo.
•The final (third or fourth) dose in the HepB series should be administered no earlier than age 24 wk.
3Diptheria and tetanus toxides and acellular perfusion vaccine (DTaP) (minimum age, 6 wk).
•The fourth dose may be administered as early as age 12 mo, provided at least 6 mo have elapsed since the third dose.
4Hemophilus influenzae type b-conjugate vaccine (Hib) (minimum age, 6 wk).
•If PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB or Comvax [HepB-Hib]) is administered at ages 2 and 4 mo, a dose at age 6 mo is not indicated.
•Hiberix should not be used for doses at ages 2, 4, or 6 mo for the primary series but can be used as the final dose in children aged 12 mo-4 yr.
5Pneumococcal vaccine (minimum age, 6 wk for pneumococcal conjugate vaccine [PCV]; 2 yr for pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV]).
•PCV is recommended for all children <5 yr. Administer one dose of PCV to all healthy children aged 24-59 mo who are not completely vaccinated for their age.
•A PCV series begun with 7-valent PCV (PCV7) should be completed with 13-valent PCV (PCV13).
•A single supplemental dose of PCV13 is recommended for all children aged 14-59 mo who have received an age-appropriate series of PCV7.
•A single supplemental dose of PCV13 is recommended for all children aged 60-71 mo with underlying medical conditions who have received an age-appropriate series of PCV7.
•The supplemental dose of PCV13 should be administered at least 8 wk after the previous dose of PCV7. See MMWR 2010:59(No. RR-11).
•Administer PPSV at least 8 wk after last dose of PCV to children aged 2 yr or older with certain underlying medical conditions, including a cochlear implant.
6Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) (minimum age, 6 wk).
•If 4 or more doses are administered prior to age 4 yr an additional dose should be administered at age 4-6 yr.
•The final dose in the series should be administered on or after the fourth birthday and at least 6 mo following the previous dose.
7Influenza vaccine (seasonal); (minimum age, 6 mo for trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine [TIV]; 2 yr for live attenuated influenza vaccine [LAIV]).
•For healthy children aged 2 yr and older (i.e., those who do not have underlying medical conditions that predispose them to influenza complications), LAIV or TIV may be used, except that LAIV should not be given to children aged 2-4 yr who have had wheezing in the past 12 mo.
•Administer two doses (separated by at least 4 wk) to children aged 6 mo-8 yr who are receiving seasonal influenza vaccine for the first time or who were vaccinated for the first time during the previous influenza season but only received one dose.
•Children aged 6 mo-8 yr who received no doses of monovalent 2009 H1N1 vaccine should receive two doses of 2010–2011 seasonal influenza vaccine.
8Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) (minimum age, 12 mo). See MMWR 2010;59(No. RR-8):33–34.
•The second dose may be administered before age 4 yr, provided at least 4 wk have elapsed since the first dose.
•The second dose may be administered before age 4 yr, provided at least 3 mo have elapsed since the first dose.
•For children aged 12 mo-12 yr, the recommended minimum interval between doses is 3 mo. However, if the second dose was administered at least 4 wk after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid.
9Varicella vaccine (minimum age, 12 mo).
•The second dose may be administered before age 4 yr, provided at least 3 mo have elapsed since the first dose.
•For children aged 12 mo-12 yr, the recommended minimum interval between doses is 3 mo. However, if the second dose was administered at least 4 wk after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid.
10Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA) (minimum age, 12 mo).
•Administer two doses at least 6 mo apart.
•HepA is recommended for children >23 mo who live in areas in which vaccination programs target older children, who are at increased risk for infection, or for whom immunity against hepatitis A is desired.
From Centers for Disease Control: www.cdc.gov/vaccines
Immunization Schedules (www.cdc.gov/vaccines) Retrieved October 31, 2011.
Centers for Disease Control: ___________Prevention of Pneumococcal Disease Among Infants and Children — Use of 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine and 23-Valent Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
December 10, 2010 / 59(RR11);1-18 MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 59(RR-11) 2010; and
Prevention and Control of Influenza with Vaccines
Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2010
August 6, 2010 / 59(rr08);1-62 Centers for Disease Control: MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 59(RR-8):33–34, 2010.
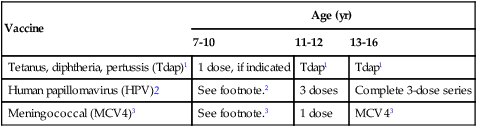
Table 16-3A
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Persons 7-18 years, United States, 2011
| Vaccine | Age (yr) | ||
| 7-10 | 11-12 | 13-16 | |
| Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (Tdap)1 | 1 dose, if indicated | Tdap1 | Tdap1 |
| Human papillomavirus (HPV)2 | See footnote.2 | 3 doses | Complete 3-dose series |
| Meningococcal (MCV4)3 | See footnote.3 | 1 dose | MCV43 |
1Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap, minimum age, 10 yr for Boostrix and 11 yr for Adacel).
• Persons aged 11-18 yr who have not received Tdap should receive a dose followed by Td booster doses every 10 yr thereafter.
• Persons aged 7-10 yr who are not fully immunized against pertussis (including those never vaccinated or with unknown pertussis vaccination status) should receive a single dose of Tdap. Refer to the catch-up schedule if additional doses of tetanus and diphtheria toxoid–containing vaccine are needed.
• Tdap can be administered regardless of the interval since the last tetanus and diphtheria toxoid–containing vaccine.
2Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. HPV4 (Gardasil) and HPV2 (Cervarix). (minimum age, 9 yr).
• Either HPV4 or HPV2 is recommended in a three-dose series for females aged 11 or 12 yr. HPV4 is recommended in a three-dose series for males aged 11 or 12 yr.
• The vaccine series can be started beginning at age 9 yr.
• Administer the second dose 1 to 2 mo after the first dose and the third dose 6 mo after the first dose (at least 24 wk after the first dose).
• See MMWR 2010;59:626-32, available at http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/wk/mm5920.pdf
3Meningococcal conjugate vaccine/MCV4, quadrivalent (minimum age, 2 yr).
• Administer MCV4 at age 11-12 yr with a booster dose at age 16 yr.
• Administer one dose at age 13-18 yr if not previously vaccinated.
• Persons who received first dose at age 13-15 yr should receive a booster dose at age 16-18 yr with a minimum interval of at least 8 wk after the preceding dose.
• If the first dose is administered at age 16 yr or older, a booster dose is not needed.
• Administer two doses at least 8 wk apart to previously unvaccinated persons with persistent complement component deficiency and anatomic or functional asplenia, and one dose every 5 yr thereafter.
• Adolescents aged 11-18 with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection should receive a two-dose primary series of MCV4, at least 8 wk apart.
• See MMWR 2011;60:72-76, available at http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/wk/mm6003.pdf and Vaccines for Children Program.
Reference: www.cdc.gov/vaccines, retrieved October 1, 2012.
From Centers for Disease Control: Vaccines and immunizations, 2012 (www.cdc.gov/vaccines).
Table 16-3B
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Persons aged 7-18 years, United States, 2012
| Vaccine | Age: 7-18 yr |
| Influenza4 | Yearly for all children |
| Pneumococcal (PCV13)5 | See footnote.5 |
| Hepatitis A (Hep A)6 | Complete 2-dose series |
| Hepatitis (Hep B)7 | Complete 3-dose series |
| Inactivated poliovirus (IPV)8 |