Fig. 37.1
Skin rash of the hand of the patient
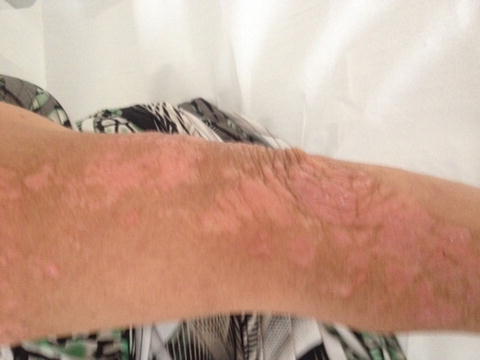
Fig. 37.2
Skin rash of the arm of the patient
In summary, this patient developed a complex combination of well-known TKI toxicities : hypertension, QTc prolongation, diarrhea, and skin rash. The recommendations on the management of these toxicities are reported in Tables 37.1, 37.2, and 37.3.
Table 37.1
Cardiotoxicity management
Cardiotoxicity (hypertension, QTc prolongation) | |
|---|---|
Prevention | • Hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia should be corrected before initiating therapy and levels maintained within the normal range throughout treatment, specifically with potassium concentrations maintained above 4 mEq/L [5] • Vandetanib should not be used in patients with a history of long QT syndrome or bradyarrhythmias [5] • Check interactions with drugs [5]a • Assess pretreatment risk with a minimum of two standardized blood pressure measurements, a thorough patient history, physical examination, and laboratory evaluation to determine specific cardiovascular risk factors [6] • Set a goal blood pressure at 140/90 mmHg for most patients, in accordance with recommendations for all adults. Higher-risk patients, including those with diabetes and/or chronic kidney disease, should achieve a lower blood pressure goal (e.g., 130/80 mmHg) [6] • Actively monitor blood pressure weekly during the first cycle of TKI therapy and then at least every 2–3 weeks for the duration of treatment [6] |
Management | • Electrocardiogram as well as serum levels of calcium, potassium, and magnesium should be obtained at baseline and during weeks 2 to 4, weeks 8 to 12, and every 3 months thereafter during therapy • Ensure that patients for whom antihypertensive therapy has already been prescribed are adherent and that therapy has been titrated to effective doses. For newly diagnosed patients with hypertension, therapy should be initiated and titrated to effective doses, ideally, before initiating TKI therapy [6] • Aggressively manage blood pressure to avoid the development of complications associated with excessive or prolonged blood pressure increases [6] • Dose reduction or discontinuation of TKI therapy may be considered if blood pressure cannot be controlled; once the desired blood pressure is achieved, TKI therapy should be reinstituted at the same or lower dose to achieve maximum efficacy on the tumor growth [6]
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|