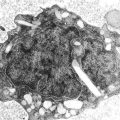
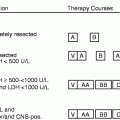
4.
Velpeau A. Sur la resorption du puseat sur l’altération du sang dans les maladies clinique de persection nenemant. Premier observation. Rev Med. 1827;2:216.
5.
Donne A. De l’origine des globules du sang, de leur mode de formation, de leur fin. C R Acad Sci. 1842;14:366.
6.
Bennett’s JH. Case of hypertrophy of the spleen and liver in which death took place from suppuration of the blood. Edinb Med Surg J. 1845;64:413.
7.
Virchow R. Weisses Blut. Frorieps Notizen. 1845;36:151.
8.
Fuller H. Particulars of a case in which enormous enlargement of the spleen and liver, together with dilatation of all vessels in the body were found coincident with a peculiarly altered condition of the blood. Lancet. 1846;ii:43.
9.
Virchow R. Weisses Blut und Milztumoren. Med Z. 1846;15:157.
10.
Wood GB. Trans Coll Physicians. Philadelphia. p. 265. 1850–52.
11.
Virchow R. Zur pathologischen Physiologie des Bluts: Die Bedeutung der milz- und Lymph-Drusen-Krankheiten fur die Blutmischung (Leukaemia). Virchows Arch. 1853;5:43.CrossRef
12.
Neumann E. Ein Fall von Leukamie mit Erkrankung des Knochenmarkes. Arch Heilk. 1870;11:1.
13.
Ebstein W. Ueber die acute Leukamie und Pseudoleukamie. Deut Arch Klin Med. 1889;44:343.
14.
Ehrlich P. Parbenanalytische Untersuchungen zur Histologie und Klinik des Blutes. Berlin: Hirschwald; 1891.
15.
Neumann E. Uber myelogene Leukamie. Berliner Klin Wochenschr. 1878;15:69.
17.
Turk W. Ein System der Lymphomatosen. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1903;16:1073.
18.
Bernard J. L’erythroleucemie experimentale provoquée par les injections intramedullaires du goudron. Sang. 1934;8:28.
19.
Storti E. Modifications morphologiques du sang et des organes hematopoietiques provoquées chez le rat blanc par injections intramedullaires de 1–2 benzopyrene. Sang. 1937;11:7.
20.
Nowell PC, Hungerford DA. A minute chromosome in human granulocytic leukemia. Science. 1960;132:1497.
21.
Fialkow PJ, Martin PJ, Najfeld V, Penfold GK, Jacobson RJ, Hansen JA. Evidence for a multistep pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1981;58:159.
22.
Stryckmans PA, Debusscher L, Collard E. Cell kinetics in chronic granulocytic leukaemia (CGL). Clin Haematol. 1977;6:21.PubMed
23.
Pederson B. Kinetics and cell function. In: Shaw MT, editor. Chronic granulocytic leukaemia. Eastbourne UK: Praeger; 1982. p. 93.
24.
25.
26.
Ben-Neriah Y, Daley GQ, Mes-Masson A-M, Witte ON, Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia specific p210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986;223:212.CrossRef
27.
Lee M-S, Stass SA. Detection of chimeric bcr-abl mRNA and minimal residual disease by polymerase chain reaction. Hematology. 1991;13:241.
28.
Marley SB, Gordon MY. Chronic myeloid leukaemia: stem cell derived but progenitor driven. Clin Sci (Lond). 2005;109:13.CrossRef
29.
30.
Bedi A, Zehnbauer BA, Sharkis SJ, Jones RJ. Inhibition of apoptosis by BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1994;15:2038.
31.
32.
33.
Osler W. Leukaemia. In: The principles and practice of medicine, 7th ed. New York: Appleton; 1909. p. 731
34.
Minot B, Isaacs R. Lymphatic leukemia: age, incidence, duration and benefit derived from irradiation. Boston Med Surg J. 1924;191:1.CrossRef
35.
36.
Galton DAG. The pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Can Med Assoc J. 1966;94:1005.PubMed
37.
Dameshek W. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia—an accumulative disease of immunologically incompetent lymphocytes. Blood. 1967;29:566.PubMed
38.
39.
Hockenberry DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin X-M, Milliman CC, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993;75:241.CrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree