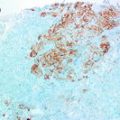
Fig. 14.1
Schematic representation biphasic progression of fibroepithelial tumors
PT is further classified into benign, borderline and malignant categories. Due to some overlapping histologic features, differentiation of FA and benign PT and accurate grading of PT may be difficult on small biopsies. Due to significant differences in their clinical behavior, complete excision of such indeterminate lesions on needle biopsies may be needed with appropriate clinical correlation for definitive classification of fibroepithelial tumors. Some immunohistochemical markers have shown promise to aid in this differential diagnosis, especially Ki67 proliferation index. But as of now, there is no “magic marker” with high sensitivity and specificity and morphology on a completely resected tumor remains the gold standard. Large scale or multi-institutional studies with long follow-up may be needed to address these issues in the future.
References
1.
2.
Noguchi S, Yokouchi H, Aihara T, Motomura K, Inaji H, Imaoka S, Koyama H. Progression of fibroadenoma to phyllodes tumor demonstrated by clonal analysis. Cancer. 1995;76(10):1779–85.PubMed
3.
Giri D. Recurrent challenges in the evaluation of fibroepithelial lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133(5):713–21.PubMed
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Noguchi S, Motomura K, Inaji H, Imaoka S, Koyama H. Clonal analysis of fibroadenoma and phyllodes tumor of the breast. Cancer Res. 1993;53(17):4071–4.PubMed
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Sawyer EJ, Hanby AM, Ellis P, Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Boyle S, Tomlinson IP. Molecular analysis of phyllodes tumors reveals distinct changes in the epithelial and stromal components. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(3):1093–8.PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
17.
Sawhney N, Garrahan N, Douglas-Jones AG, Williams ED. Epithelial–stromal interactions in tumors. A morphologic study of fibroepithelial tumors of the breast. Cancer. 1992;70(8):2115–20.PubMed
18.
Paul S, Dey A. Wnt signaling and cancer development: therapeutic implication. Neoplasma. 2008;55(3):165–76.PubMed
19.
20.
21.
Mahipal A, Kothari N, Gupta S. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: coming of age. Cancer Control. 2014;21(1):74–9.PubMed
22.
Kersting C, Kuijper A, Schmidt H, Packeisen J, Liedtke C, Tidow N, Gustmann C, Hinrichs B, Wulfing P, Tio J, et al. Amplifications of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene (egfr) are common in phyllodes tumors of the breast and are associated with tumor progression. Lab Invest. 2006;86(1):54–61.CrossRefPubMed
23.
Zelada-Hedman M, Werer G, Collins P, Backdahl M, Perez I, Franco S, Jimenez J, Cruz J, Torroella M, Nordenskjold M, et al. High expression of the EGFR in fibroadenomas compared to breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1994;14(5A):1679–88.PubMed
24.
25.
Dai N, Rapley J, Angel M, Yanik MF, Blower MD, Avruch J. mTOR phosphorylates IMP2 to promote IGF2 mRNA translation by internal ribosomal entry. Genes Dev. 2011;25(11):1159–72.PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
26.
Liao B, Hu Y, Herrick DJ, Brewer G. The RNA-binding protein IMP-3 is a translational activator of insulin-like growth factor II leader-3 mRNA during proliferation of human K562 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(18):18517–24.CrossRefPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree