G
gabapentin
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
|---|---|
| 60 ml/min or higher | 400 mg q8h |
| 30-59 ml/min | 300 mg q12h |
| 16-29 ml/min | 300 mg daily |
| less than 16 ml/min | 300 mg every other day |
| Hemodialysis | 200-300 mg after each 4-hr hemodialysis session |
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Urinary incontinence
Use with caution in older patients with: Renal impairment, Urinary incontinence
1 Brodie M, Kwan P. Epilepsy in elderly people. BMJ. 2005;331:1317-1322.
2 Rowan AJ, Ramsay RE, Collins JF, et al. New onset geriatric epilepsy: a randomized study of gabapentin, lamotrigine, and carbamazepine. Neurology. 2005;64:1868-1873.
3 Arroyo S, Kramer G. Treating epilepsy in the elderly: safety considerations. Drug Safety. 2001;24:991-1015.
4 Drugs that may cause cognitive disorders in the elderly. Med Lett. 2000;42:111-112.
5 Willmore LJ. Choice and use of newer anticonvulsant drugs in older patients. Drugs Aging. 2000;17:441-452.
6 Faught E. Epidemiolgy and drug treatment of epilepsy in elderly people. Drugs Aging. 1999;15:255-269.
galantamine hydrobromide
(ga-lan’-ta-meen hye-droe-broe’-mide)
 Brand Name(s): Razadyne, Razadyne ER
Brand Name(s): Razadyne, Razadyne ER
 Contraindications: Severe hepatic or renal impairment
Contraindications: Severe hepatic or renal impairment
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
ganciclovir sodium
(gan-sye’-kloe-veer soe’-dee-um)
 Brand Name(s): Cytovene, Vitrasert
Brand Name(s): Cytovene, Vitrasert
 Contraindications: Absolute neutrophil count less than 500/mm3, platelet count less than 25,000/mm3, hypersensitivity to acyclovir or ganciclovir, immunocompetent patients, patients with congenital CMV disease
Contraindications: Absolute neutrophil count less than 500/mm3, platelet count less than 25,000/mm3, hypersensitivity to acyclovir or ganciclovir, immunocompetent patients, patients with congenital CMV disease Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
gatifloxacin
 Brand Name(s): Tequin, Tequin Teqpaq, Zymar
Brand Name(s): Tequin, Tequin Teqpaq, Zymar
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
|---|---|
| 40 ml/min | 400 mg/day |
| less than 40 ml/min | Initially, 400 mg/day, then 200 mg/day |
| Hemodialysis | Initially, 400 mg/day, then 200 mg/day |
| Peritoneal dialysis | Initially, 400 mg/day, then 200 mg/day |
 Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to quinolones
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to quinolones
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
gemfibrozil
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
gemifloxacin mesylate
(gem-ah-flox’-a-sin mes’-sil-ate)
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
|---|---|
| greater than 40 ml/min | 320 mg once a day |
| 40 ml/min or less | 160 mg once a day |
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
gentamicin sulfate
 Brand Name(s): Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Garamycin Topical, Genoptic, Gentacidin, Gentak, Ocu-Mycin
Brand Name(s): Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Garamycin Topical, Genoptic, Gentacidin, Gentak, Ocu-MycinRx: with prednisolone (Pred-G)
Chemical Class: Aminoglycoside
 Brand Name(s): Neurontin
Brand Name(s): Neurontin Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of bipolar disorder, chronic pain, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, essential tremor, hot flashes, hyperhidrosis, migraines, psychiatric disorders (social phobia)
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of bipolar disorder, chronic pain, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, essential tremor, hot flashes, hyperhidrosis, migraines, psychiatric disorders (social phobia) Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Neuropathic Pain, Post-Herpetic Neuralgia, Essential Tremor
Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Neuropathic Pain, Post-Herpetic Neuralgia, Essential Tremor Side Effects:
Side Effects: Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Dosage adjustments required in older adults with creatinine clearance < 60 ml/min. Gabapentin has been well-studied in older adults and is considered a first-line agent as a result of tolerability, small effects on cognition, and few drug interactions. Absorption is reduced by approximately 50% at doses > 3600 mg/day. Capsules are large and may be difficult to swallow, especially in patients with dysphagia or dry mouth.
Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Dosage adjustments required in older adults with creatinine clearance < 60 ml/min. Gabapentin has been well-studied in older adults and is considered a first-line agent as a result of tolerability, small effects on cognition, and few drug interactions. Absorption is reduced by approximately 50% at doses > 3600 mg/day. Capsules are large and may be difficult to swallow, especially in patients with dysphagia or dry mouth. Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions

 Use with caution in older patients with: None
Use with caution in older patients with: None U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: None
Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: None Side Effects:
Side Effects: Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Galantamine, like other cholinesterase inhibitors, is modestly effective for treatment of cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Compared to placebo, persons using galantamine have less decline in performance on cognitive tests, but most patients derive minimal clinical benefit, and there is no evidence the drug delays disability or institutionalization. Galantamine is expensive, and not cost-effective for this indication. Persons using drugs to treat Alzheimer’s disease should be monitored closely, and prescribers should have a low threshold for discontinuing these agents if no clinical benefit is observed.
Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Galantamine, like other cholinesterase inhibitors, is modestly effective for treatment of cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Compared to placebo, persons using galantamine have less decline in performance on cognitive tests, but most patients derive minimal clinical benefit, and there is no evidence the drug delays disability or institutionalization. Galantamine is expensive, and not cost-effective for this indication. Persons using drugs to treat Alzheimer’s disease should be monitored closely, and prescribers should have a low threshold for discontinuing these agents if no clinical benefit is observed. Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages:
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of other CMV infections, such as gastroenteritis, hepatitis, and pneumonitis
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of other CMV infections, such as gastroenteritis, hepatitis, and pneumonitis Side Effects
Side Effects Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance: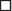

 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages:

 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Brand Name(s): Lopid
Brand Name(s): Lopid Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Contraindications: Liver dysfunction (including primary biliary cirrhosis), preexisting gallbladder disease, severe renal dysfunction
Contraindications: Liver dysfunction (including primary biliary cirrhosis), preexisting gallbladder disease, severe renal dysfunction Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Brand Name(s): Factive
Brand Name(s): Factive Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Contraindications: Concurrent use of amiodarone, quinidine, procainamide, or sotalol; history of prolonged QTc interval; hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones; uncorrected electrolyte disorders (such as hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia)
Contraindications: Concurrent use of amiodarone, quinidine, procainamide, or sotalol; history of prolonged QTc interval; hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones; uncorrected electrolyte disorders (such as hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia) Side Effects
Side Effects

 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology:


