Classification: ICD-9 042-044; ICD-10 B20-24
Syndromes and synonyms: VIH, SIDA, slim disease, acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
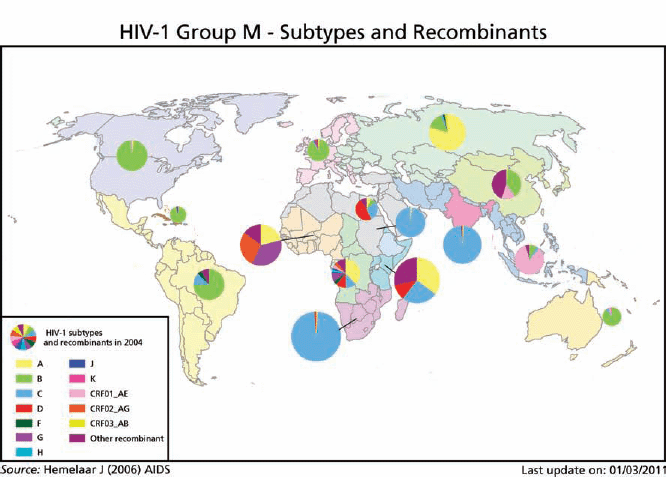
Agent: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), an enveloped single-stranded RNA virus of the Lentivirus genus and Retroviridae family, is divided into two main species HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is more infectious and more virulent than HIV-2 and predominates globally, with HIV-2 transmission restricted to parts of Western and Central Africa.
Reservoir: Humans.
Transmission: HIV is transmitted through contact with HIV-infected body fluids (blood, semen, and vaginal secretions) and is predominantly a sexually transmitted infection. Other routes are: sharing contaminated needles; mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding; blood or blood product transfusion; and organ or tissue transplantation.
Incubation period: Around 50–70% of infected individuals develop a self-limiting ‘primary’ HIV illness 1–12 weeks after infection. Time from infection to development of clinically apparent immunodeficiency ranges from less than 1 year to over 15 years.
Clinical findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




