Endometrial and Cervical Cancers
Cancer Treatment Centers of America and Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Cervical Cancer
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following combination chemotherapy regimens has been shown in a phase III randomized trial to result in a superior survival outcome compared to single-agent cisplatin when employed as a component of a chemoradiation strategy in locally advanced cervical cancer?
- Cisplatin–gemcitabine
- Cisplatin–paclitaxel
- Cisplatin–topotecan
- None of the above
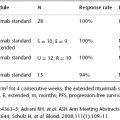
A phase III randomized trial conducted in South America has revealed the superiority of the combination of cisplatin plus gemcitabine compared to cisplatin alone when employed as a component of a concurrent chemoradiation strategy. Despite this outcome, this strategy has not been adopted for routine use as several groups have found excessive toxicity associated with this chemotherapy combination when added to external-beam radiation.
2. Despite the favorable survival outcome in this phase III trial, the study results have been criticized for which of the following reasons?
- A higher-than-expected percentage of patients in the cisplatin-only arm being more than 65 years of age
- A higher-than-expected percentage of patients in the combination chemotherapy arm who had not previously received external-beam radiation
- A higher than expected percentage of patients in both study arms who were HIV-positive
- A large percentage of patients had previously received cisplatin as a component of a chemoradiation program
While this is not the fault of the study investigators, the relevance of this study has been questioned because a substantial proportion of individuals entered into the trial had previously received (and failed) a cisplatin-containing chemoradiation program. Thus, one rational interpretation of this study is that it actually compared “single agent topotecan” to “no chemotherapy” rather than defining the activity of this combination cisplatin-based regimen.
3. In a multi-arm phase III trial in metastatic and recurrent cervical cancer, which of the following regimens was shown to result in a statistically significant improvement in time to disease progression compared to the other study arms?
- Cisplatin–paclitaxel
- Cisplatin–gemcitabine
- Cisplatin–topotecan
- None of the above
In this landmark Gynecologic Oncology Group study, there was no statistically significant difference in either time to disease progression or overall survival in any of the study arms (cisplatin–paclitaxel, cisplatin–gemcitabine, cisplatin–topotecan, or cisplatin–gemcitabine).
4. In the above-noted study, which of the following clinical factors were NOT found to negatively impact a patient’s opportunity to achieve a clinical response to cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy?
- Prior documented human papilloma virus (HPV) infection
- Prior chemoradiation
- Disease in a previously radiated region
- None of the above
Both prior chemoradiation and disease in a previously radiated area will negatively impact the opportunity for a response to platinum-based systemic therapy for metastatic or recurrent cervical cancer.
5. What noncytotoxic agent, when combined with chemotherapy, has been shown in a phase III randomized trial to improve survival in metastatic or recurrent cervical cancer?
- Erlotinib
- Venurafinib
- Bevacizumab
- Gefitinib
In a report of a phase III randomized trial, the addition of bevacizumab to combination chemotherapy was shown to result in a statistically significant improvement in overall survival in metastatic and recurrent cervical cancer. This was the first randomized trial to document the utility of a noncytotoxic agent in this clinical setting.
6. Cisplatin has been recognized for more than 30 years to be an important agent in the management of cervical cancer. Which of the following strategies has NOT been established as being an effective cisplatin-based approach to improve survival in cervical cancer?